Transformer & Transformer Components
(9801 products)2 In 1 Transformer Efficiency: 98%
40000 INR (Approx.)/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Cooling TypeOil & Air Cooled
Rated Voltage11000/433 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, transformer
Output415, 440V
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency98%
Isolation Transformers - High-Performance Electrical Insulation , Enhanced Voltage Stability and Noise Reduction
Price: 500000 INR/Piece
MOQ5 Piece/Pieces
Product DescriptionIsolation Transformers
Multi Color Mild Steel Material 24 V Lighting Transformer
Product TypeOther, 24 V Lighting Transformer
MaterialMetal
UsageIndustrial
Honeywell Ignition Transformer - Single Phase, Electrical Power Range | Burner Ignition Efficiency, High Quality Performance
Price: 2000 INR/Unit
MOQ10 Unit/Units
Product TypeOther, Honeywell Ignition Transformer
PhaseSingle Phase
UsageBurner Ignition
Power ScopeElectrical
Transformer Air Cell - Polyamide Fabric with Copper Core, Laminated Structure, for Insulating Oil Preservation
Price: 200.00 INR/Piece
MOQ500 Piece/Pieces
Voltage Booster TypeInsulation Oil
Coil MaterialCopper Core
Product TypeIsolation Transformer
MaterialRubber
UsageFor Industrial Purpose
Coil StructureLaminated Core
Softex Industrial Products Pvt. Ltd.
Kolkata
Current Transformer Upto 145 Kv - Material: Metal
Price: 130000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Voltage Booster TypeDry
Cooling TypeOil Cooled
Product TypeOther, Current Transformer upto 145 kV
MaterialMetal
PhaseSingle Phase
UsageIndustrial
Straton Electricals Private Limited
Hyderabad
Packaged Electrical Substation - Stainless Steel, Up to 2000 KVA, 11 KV Class | Eco-Friendly, High Efficiency, Low Noise, PLC Control, Touch Screen, Extended Warranty 1+1 Year
Price: 1000000 INR/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Colorother
Product TypePackaged substation
General UseAuxiliary Equipment-Utility Equipment
MaterialOther, Stainless steel
TypeBroaching, Drilling, Milling, Etching, Other, Turning, Laser Machining, Chemical Machining
ComputerizedYes
Assembled Bushings
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
FOB PortEx-Works
Payment TermsCash on Delivery (COD), Others, Cash Advance (CA)
Packaging DetailsAppropriately packed
Ctr Manufacturing Industries Private Limited
Pune
Single Phase Manual Dj Voltage Transformer - Efficiency: Above 90%
Price: 8000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Rated Voltage120-300 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, Voltage Transformer
Output5 to 15 kVA
Efficiencyabove 90%
PhaseSingle Phase
Protekg Power Electronics Private Limited
Ahmedabad
Distribution Transformer - Frequency (Mhz): 50/60 Hertz (Hz)
Cooling TypeAir Cooling
Voltage Booster TypeDry
MaterialMild Steel
OutputAC
Frequency (MHz)50/60 Hertz (HZ)
PhaseThree Phase
Ests Power Transformer Private Limited
Ghaziabad
Power Electrical Substation Efficiency: 99.9%
Price: 1000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
MaterialCopper
OutputAs per customer requirement
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency99.9%
Urja Techniques (india) Pvt. Ltd.
Mumbai
Vertical Package Substation
Price: 3000000 INR/Piece
MOQ10 Piece/Pieces
Main Export Market(s)Australia, Central America, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Asia, Africa
Main Domestic MarketAll India
Auto / Isolation Transformer For Cnc Machines Coil Material: Copper Core
Price Trend: 40000 - 53000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Inch/Inches
Coil MaterialCopper Core
Operating Temperature0 -50 Celsius (oC)
Cooling TypeAir Cooled
Voltage Booster TypeOther
Product TypeIsolation Transformer
MaterialCopper
Adroit Power Systems India Pvt. Ltd.
Coimbatore
Electrical H.T Porcelain Transformer Bushings
Product TypeOther, Electrical H.T Porcelain Transformer Bushings
Gate Drive Transformer - Frequency (Mhz): 2000 Kilohertz ( Khz )
MOQ100 Unit/Units
MaterialMetal
Frequency (MHz)2000 Kilohertz ( KHZ )
PhaseSingle Phase
UsageIndustrial
Coil StructureToroidal
Distribution Transformer - Efficiency: 97%
Price: 408900 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Rated Voltage220-440 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, Distribution Transformer
MaterialMild Steel
Output400 or 415V
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency97%
Hindustan Power Products (p) Ltd.
Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller18 Years
Uv Transformer - Premium Quality Crude Materials , Versatile for Various Market Needs
Product DescriptionWe are Exporting, Manufacturing and Supplying an collection of Uv Tranformer in Faridabad, Haryana, India. It is manufactured from premium quality crude materials and latest know-how. Effortlessly appropriate at various types of market ordered to provide features and requirements to meet up with up
Step down transformer
Price: 150000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Supply Ability100 Per Day
Delivery Time15 Days
Main Export Market(s)Asia, Australia, Central America, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa
Gujarat Plug-in Devices Pvt. Ltd.
Vadodara
Unitized Substation Efficiency: 98%
Price Trend: 1000000.00 - 10000000.00 INR/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Current TypeAC
DisplayMeter
Output Voltage11 Volt (V)
Rated Voltage11000/433 Volt (V)
Product TypeSubstation
Control SystemManual
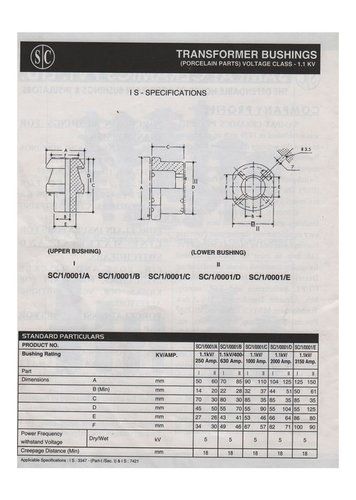
1.1 Kv Transformer Bushings Of Voltage Class - Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price: 15 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Rated Voltage220 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, Transformer Bushings
MaterialPorcelain
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
PhaseSingle Phase
UsageTransformer
Sampat Ceramics Pvt. Ltd.
Kolkata
 Super Premium
Super Premium13 Years
 Super Premium
Super PremiumInstrument Transformer - Usage: Electrical
Price: 20000 INR/Plant
MOQ1 Plant/Plants
Product TypeOther, Instrument Transformer
MaterialMetal
Frequency (MHz)50-60 Hertz (HZ)
EfficiencyHigh
UsageElectrical
Power ScopeElectrical
Air Cooled Welding Transformer
Price: 72000 INR/Unit
MOQ2 Unit/Units
Product TypeOther, Air Cooled Welding Transformer
MaterialMetal
PhaseThree Phase
Ss Gas Burner Ignition Transformers
Price: 1800 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeOther, Gas Burner Ignition Transformers
MaterialSS
PhaseSingle Phase
UsageIn Door or Out Use
Weight0.1-1000 Grams (g)
1000kVA 3-Phase Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer
Price: 1400000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Main Domestic MarketAll India
Electrical Power Transformer - Efficiency: 50-100 %
Price: 3000000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
High Voltage480 Volt (V)
Voltage Booster TypeInsulation Oil
Rated Voltage240 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, Electrical Power Transformer
MaterialMild Steel
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Substation Electrical Power Transformer Efficiency: High
Price: 1500000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Rated Voltage440 Volt (V)
Cooling TypeOil Cooled
MaterialMetal
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
EfficiencyHigh
PhaseThree Phase
Industrial Isolation Transformer - Coil Material: Silicon Steel
Price: 995000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Number
Coil MaterialSilicon steel
Voltage Booster TypeInsulation Oil
Product TypeIsolation Transformer
Materialstainless steel
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
PhaseThree Phase
Step-up Transformer with single phase and three phase
Price Trend: 4900.00 - 5500.00 USD ($)/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Supply Ability6000 Per Month
Delivery Time7 Days
Hot Die Steel Bar (H13 Grade) - Metal Round Bars in Standard Sizes | ISO 9001:2008 Certified, Suitable for Industrial Applications
Price: 150 INR/Kilograms
MOQ100 Kilograms/Kilograms
Product TypeOther, Hot Die Steel Bar
MaterialMetal
UsageIndustrial
Latest From Transformer & Transformer Components
Standard Transformer
By:
Altime Power Systems Pvt Ltd.
DC Electrical Transformer & Transformer Components
By:
Chakraborty Electricals Pvt. Ltd.
Ready To Ship Transformer & Transformer Components
Transformer & Transformer Parts And Its Function
Introduction
If you need to move electricity from one circuit to another without affecting the frequency of the electricity, you need a transformer. As a means of reducing the amount of energy lost in transmission, it can be used to either increase or decrease the voltage in a circuit.
Parts & Functions
1. Radiator & Fans
In order to dissipate the heat produced by the core and windings, the hot oil is circulated through a system of cooling tubes.
2. Explosion Vent
The explosion vent's primary role is to prevent the power transformer from exploding should pressure in the main tank rise dangerously high as a result of severe internal malfunctions.
3. Breather
The breather's primary role is to provide dry, ambient air to the conservator tank throughout the transformer's thermal cycling.
4. Oil Conservator
The oil conservator tank is there to make sure there's enough room for the oil in the transformer to expand and contract as needed due to the fluctuating temperature of the oil in the main tank.
5. Buchholz Relay
Whether it's a short circuit fault, an inter-turn fault, or anything else, the Buchholz relay is there to keep the transformer safe.
6. Tap Changer
To adjust the transformer's output voltage, a tap changer modifies the turn ratio.
7. Transformer Oil
In addition to cooling the device, the chemical characteristics and high dielectric strength of transformer oil serve to insulate the windings.
8. Terminals and Bushings
As insulators, bushings are often fabricated from porcelain or epoxy resins. The wires that go between the terminals and the windings can travel through them without fear of damage.
9. Windings
Each winding is made up of many bundles of copper coil turns that are joined to one another. Both the input-output supply and the voltage range can influence the choice of windings. Primary and secondary windings are the input and output windings of a transformer, respectively, and are categorized based on supply. However, windings can be broken down into high-voltage windings and low-voltage windings according to the voltage range over which they operate.
10. Main Tank
They have integrated cooling tubes and lifting eyes for easy transport. Aluminum sheets are being used instead of steel plates to reduce overall weight and stray loss.
11. Cooling Tubes
For the purpose of keeping the oil in a transformer at a manageable temperature, cooling tubes are employed. It's possible for the oil in the transformer to move about on its own, or for the circulation to be pushed. With natural circulation, when the oil heats up, the hot oil rises to the top, and the cold oil sinks to the bottom; with forced circulation, a perpetual pump is utilized.
Different Types of Transformer Parts
Through electromagnetic induction, transformers are used to move electricity from one circuit to another. Step-up and step-down voltage converters are utilized for those purposes. Transformers are complex devices that rely on the coordinated efforts of their many individual pieces to perform their intended tasks. This consists of the windings, Buchholz Relay, transformer oil, tap changer, insulating materials, conservator, breather, core, cooling tubes, and explosion vent. A transformer's core, windings, insulating materials, and transformer oil are standard in all except the largest of transformers (often those with a KVA rating of 50 or above).
Function of Transformer
Voltage can be "stepped down" with a transformer to lower it, or "stepped up" to raise it. With the help of transformers, we can get the power we need, when we need it. As electricity goes from a power plant to a residence, business, or other location, transformers step in to increase the voltage and frequency of the current. A portion of the electricity that leaves a power plant and travels through transmission cables is lost. In order to minimize energy loss, utilities employ extremely high voltage. Multiple transformer kinds are utilized along the trip. Transformers increase the voltage of energy so that it may be transmitted safely and effectively as it leaves a power plant. Energy is sometimes amplified to hundreds of volts as it leaves the power plant.
Transmission stations are the last stop for electricity before it is reduced to safe levels by transformers and control equipment. Transmission line voltage is lowered even further by Transformer & Transformer Components mounted on utility poles along the route. When power is transmitted to a building, it is reduced to 120 V by a step-down transformer. Some appliances and outlets will work with a voltage of 120 V. Many electronic equipment, including computers, require a DC power source, so an adapter may be necessary.
Finally, transformers are used to reduce the voltage before it enters your home. Your home's "step-down" transformer reduces the 440-volt electricity from the power cables to the safer 120-volt level. Either the current is used directly, as in the case of light bulbs, or it is converted to direct current (DC) by means of an alternating current to a direct current (AC/DC) adapter, as in the case of laptop computers.
Transformer Applications
1. Ammeters or Current Transformers
Transformers are essential to the general operation of ammeters, voltmeters, and other measuring gadgets and devices. An ammeter is a device that measures the amount of current flowing through a circuit in real-time. There are two ways to connect ammeters to a circuit: in series if the current is relatively small, or through a measuring type current transformer if the current is large.
2. Coolant
A cooling effect can be produced by using a transformer in its air-dry configuration. Refrigerators can make efficient use of transformers' ability to produce a cooling effect by storing perishables at cool, steady temperatures.
3. Audio Transfer
An audio transformer is a type of electrical transformer used to match the impedance values of the source and the load and to isolate the signals traveling through the circuits. Audio transformers are commonly found in microphones, loudspeakers, audio amplifiers, and other similar devices.
4. Controlling The Flow of Electricity Via A Circuit
When a user needs complete control over the direction of current in a circuit but doesn't want to rely on switches or breaker panels, a transformer can be used instead. Therefore, a transformer can be used to turn on or off any electronic device.
5. Electrolysis
Typically, transformers are used in the operation of electrolysis, which is a chemical engineering application. Electrolysis, in its simplest form, is the process of separating a homogeneous or non-homogeneous mixture of elements and compounds by dissociating ionic substances into simpler substances.
6. Steel Manufacturing
Transformers are widely used in commercial applications, and one obvious place to see them in action is in steel mills. The steelmaking process involves the essential steps of melting, welding, molding, and cooling the raw material. While a high-magnitude current is needed for melting and welding the elements, a lower-magnitude current is preferred for cooling them down.
7. Charging Batteries
To add to the long list of commonplace uses for transformers, consider the act of charging a battery. To charge a battery, electrons must be sent from an electrical generator to the battery itself.
8. Alternating Current Regulation
The term "alternating current" refers to a type of electric current whose magnitude and direction alternate at regular intervals in time. An alternating current's full waveform can be simplified to a peak and trough. Here, the peak represents the largest signal amplitude, or largest current value, while the trough represents the smallest signal amplitude or smallest current magnitude.
9. Air Conditioner
Another commonplace device that relies on transformers for basic functionality is the air conditioner. The transformer in an AC unit performs a number of important tasks, such as regulating the amount of power flowing through the circuit board, allowing the fan and AC to run at the same time, and transforming the magnitude of the voltage delivered by the circuit to the AC unit to the optimal value desired by the user.
10. Stabilizer
Another common real-world application for transformers is in stabilization circuits. In order to ensure the safe operation of electrical appliances that require high current or voltage, a stabilizer circuit is typically connected to them. Primarily, a stabilizer circuit converts the signal from a household power source into a signal that is roughly equivalent to the ideal electrical demands of the system.
11. Optimize The Voltage Levels
The primary function of a transformer is to regulate the voltage levels in a circuit. To achieve this goal, transformers often amplify or reduce a portion of the input signal value to produce an output of the required magnitude.
FAQs: Transformer & Transformer Components
Q. What is a transformer used for?
Ans. A transformer is a machine that changes the voltage of an alternating current circuit so that it can be used in another circuit, or in many circuits with different voltage requirements.
Q. Does a transformer work with ac or dc?
Ans. Because of its construction, a transformer can only be used with alternating current (AC) and not direct current (DC).
Q. What are the industrial applications of transformers?
Ans. Biochemical, aerospace, manufacturing industries, and telecommunication are the industries where transformers are widely used for generating electricity, decreasing the voltage of power circuits, and charging heavy batteries.
Q. How can we get details of transformer manufacturers and suppliers in India?
Ans. Trade India is a perfect setup to get true detail about transformer manufacturers and brands in India. It has a wide range of suppliers all over India.
Manufacturers & Suppliers of Transformer & Transformer Components
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Linear Systems Mumbai, India | 24 Years |
Neo Tele-Tronix Pvt. Ltd. Kolkata, India | 23 Years |
Jindal Rectifiers Faridabad, India | 20 Years |
Softex Industrial Products Pvt. Ltd. Kolkata, India | 19 Years |
Steel Mart Mumbai, India | 19 Years |
Urja Techniques (India) Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai, India | 18 Years |
Hindustan Power Products (P) Ltd. Delhi, India | 18 Years |
Unique Engineering Works Chennai, India | 17 Years |
Servokon Systems Limited Ghaziabad, India | 16 Years |
Futuristic Technologies Ahmedabad, India | 15 Years |
Popular Products