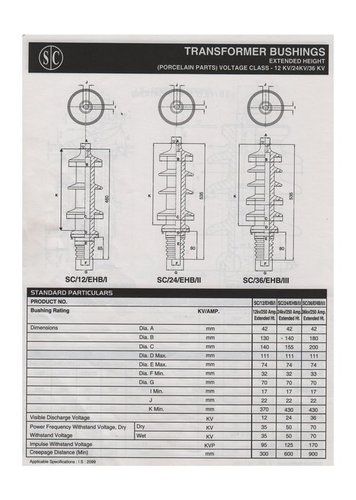
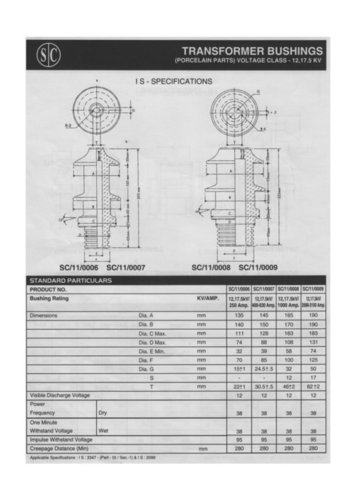
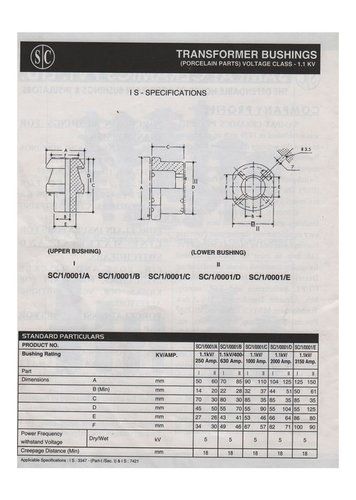
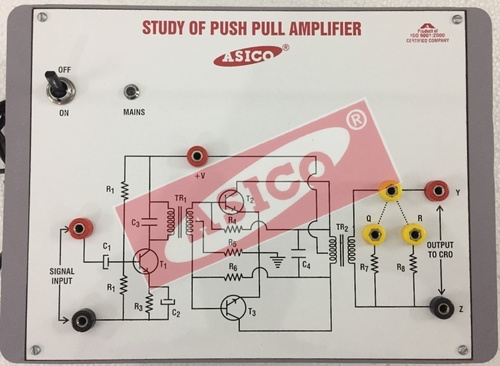
- Tradeindia
- Transformer & Transformer Components
- Transformers
Transformers - Ventilated Transformer Prices, Manufacturers & Suppliers
(12765 products)Distribution Transformer - Copper & Steel, 25 KVA to 10 MVA, Voltage Class 1.1kV to 66kV, Low Voltage Class 380V to 440V | High Efficiency, Low Losses, Customizable, Easy Installation, BIS Certified
500000 INR/Piece
MOQ5 Piece/Pieces
Supply Ability10 Per Day
Delivery Time3 Days
View More

Constant Voltage Transformers - Robust Electrical Design | Optimized Energy Efficiency, Low Voltage Regulation
Price : 500000 INR
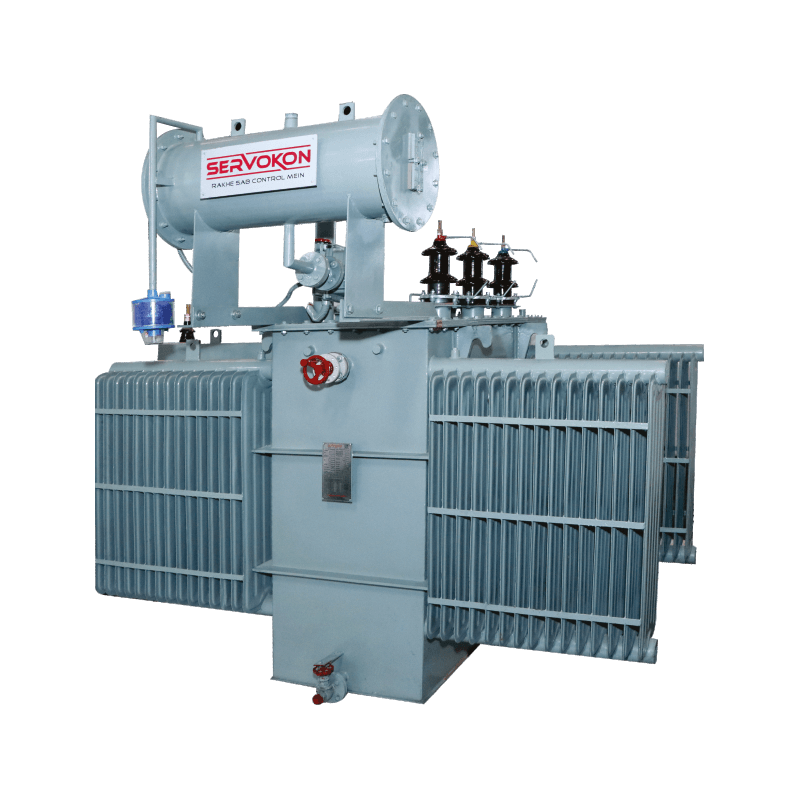

Inverter Duty Solar Transformer
Price : 500000 INR

Isolation Transformers - High-Performance Electrical Insulation , Enhanced Voltage Stability and Noise Reduction
Price : 500000 INR
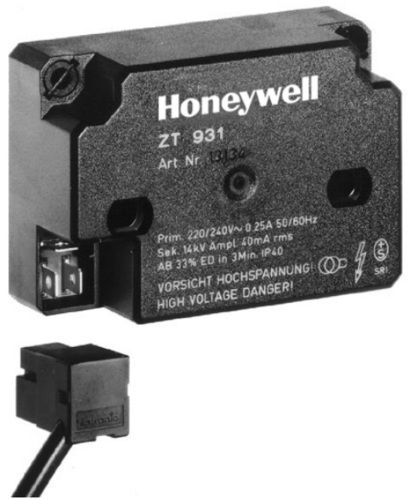
Honeywell High Frequency Ignition Unit
Primary voltage220/240V
Secondary voltage14kV
Primary current0.25A
Secondary current40mA
Protection classIP40
MaterialPlastic
Futuristic Technologies
Ahmedabad
 Super Bonanza
Super Bonanza Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Premium
Super Premium15 Years
Rectifier Set Porcelain Transformer - Application: High Voltage
MOQ10 , Piece/Pieces
SizeStandard
Product TypeRectifier Set Porcelain Transformer
MaterialPorcelain
Rated Voltage220-440 Volt (V)
ApplicationHigh Voltage, electricity equipment and electrical appliances
ColorBrown
Step Up / Step Down Transformer Air Cooled - Efficiency: 98 - 99%
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Cooling TypeNatural Air Cooled
Power Rating15 - 150 kVA
OutputAs per your machine requirement (Phase to Phase), Star / Delta connection
Frequency (MHz)47Hz to 63Hz Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency98 - 99%
PhaseThree Phase
Hindustan Power Products (p) Ltd.
Jhajjar
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Premium
Super Premium18 Years
View More

Distribution Transformer - Efficiency: 97%
Price : 408900 INR
Solar Application Transformer - Copper Material, 50 HZ Frequency | 99.9% Efficiency, Noiseless Operation, Low Maintenance, Longer Service Life, Anti-Abrasion Design
Price: /Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
MaterialCopper
OutputProduct wise
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency99.9%
Urja Techniques (india) Pvt. Ltd.
Mumbai
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Seller
Super Seller18 Years
View More

Neutral Earthing Transformer Efficiency: 99.9%
Get Best Deal

Shunt Reactor - Up to 2 MVA, 33 KV Voltage Capacity | Automatic On/Off Cooling Feature, Durable Design
Get Best Deal

Precision Converter Duty Transformer
Get Best Deal

Special Power Transformer Efficiency: 99.9%
Get Best Deal

High Power Transformers Efficiency: 99.9%
Price : 300000 INR
UL Approved Transformers - Heavy-Duty Steel Housing, 1000VA Capacity, Energy Efficient Operation, Compact Design
Price: 10000.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Rated Voltage230V / 415V
CapacityCustom as per requirement
Load LossLow
Voltage Booster TypeOther, Auto / Isolation / Step Down / Step Up
High VoltageUp to 11 kV
Dimension (L*W*H)Customized / As per design
Gujarat Plug-in Devices Pvt. Ltd.
Vadodara
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Seller
Super Seller12 Years
View More

Cast Resin Transformers - High Durability Material , Compact Design for Efficient Power Distribution
Price : 10000.00 INR

Control Transformers - 5VA to 5 KVA , Excellent Quality Phase Control and Isolation Types
Get Best Deal
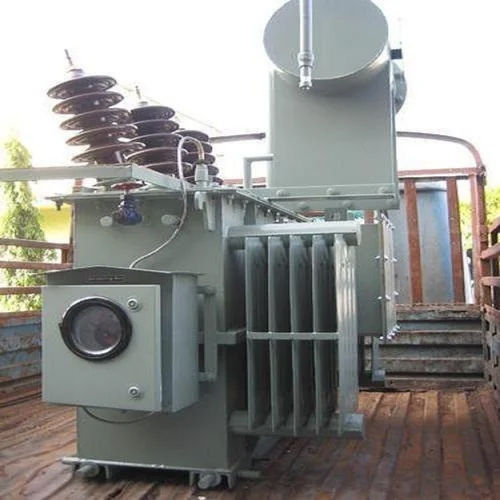

K Rated Transformer - Phase: Three Phase
Get Best Deal
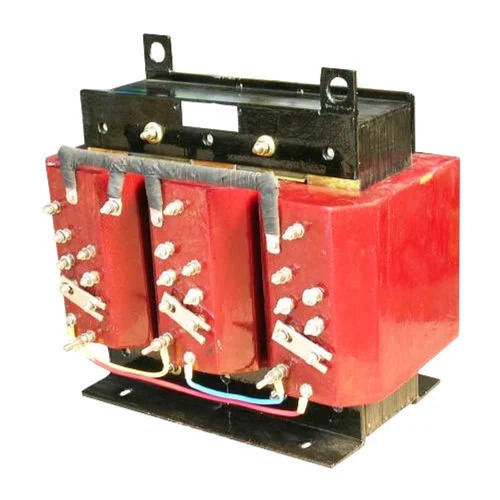

Resin Encapsulated Transformer - High Insulation Performance , Enhanced Durability and Thermal Resistance
Price : 1000.00 INR
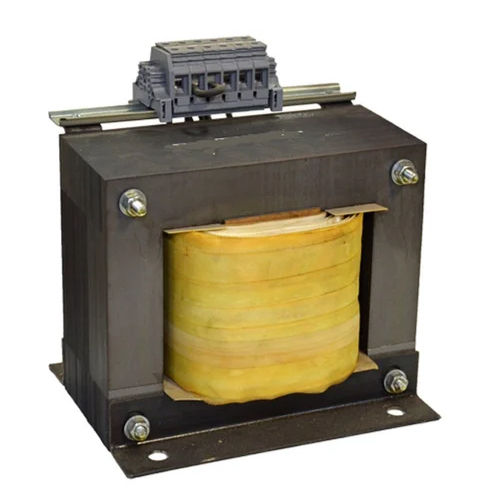

Single Phase Transformer - Frequency (Mhz): 50/60 Hz Hertz (Hz)
Price : 10000 INR
Steel Radiators
Price Trend: 5000-100000 INR/Ton
MOQ100 Ton/Tons
MaterialHigh-grade Steel
Water Content0.8 L/section
Central Distance600 mm
Working Pressure0.6 MPa
Rough Weight1.2 kg/section
Thermal Pressure1.0 MPa
Thermocool Engineering Pvt Ltd
Kolkata
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Seller
Super Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller18 Years
View More
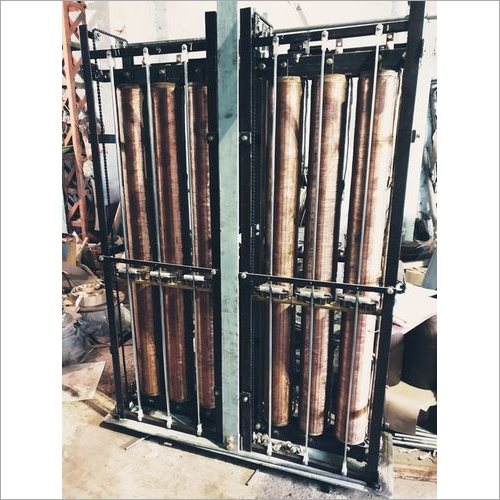

Auto Voltage Regulator - Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 600000 INR
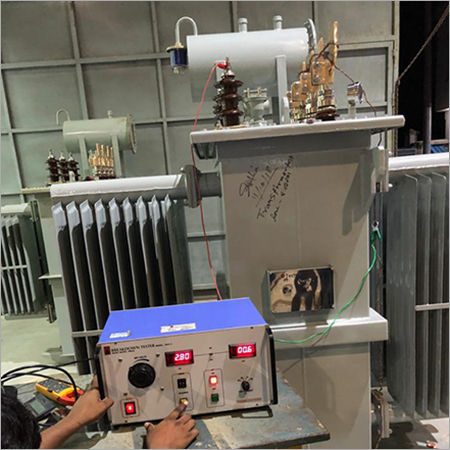

Power Transformer - Silicon Steel Core, Corrugated Steel Tank, Oil-Filled, 10-100kVA | Low Noise Design, Anti-Theft Structure, IEC 60076 Compliance
Price : 1000000-15000000 INR
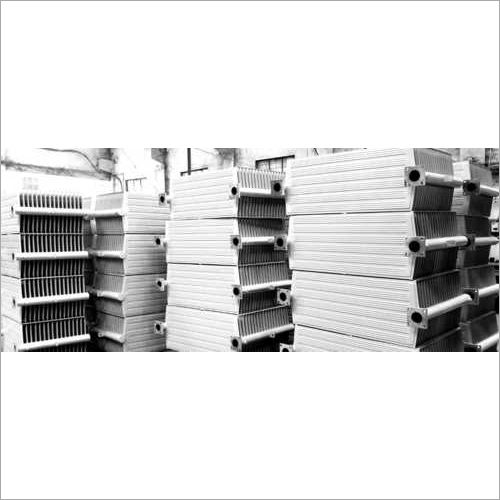

Flange Type Transformer Radiator - Durable Steel, Compact Design | Enhanced Heat Dissipation & Corrosion Resistance
Price : 10000-100000 INR
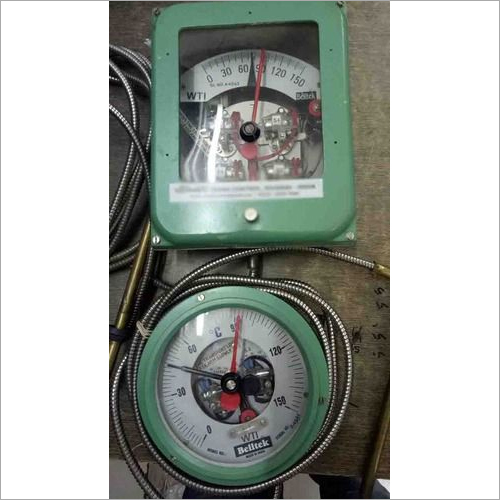

Transformer Winding Temperature Indicator
Price : 5000-15000 INR
Electrical Double Secondary Transformers Coil Material: Copper Core
Price: 50000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Coil MaterialCopper Core
Rated Voltage240 - 480 Volt (V)
Voltage Booster TypeInsulation Oil
Product TypeElectrical Transformer
MaterialMild Steel
PhaseSingle Phase
Abc Transformers Pvt. Ltd.
Noida
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Seller
Super Seller7 Years
View More
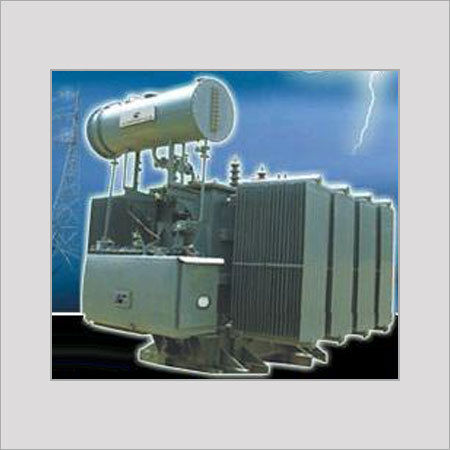

Low Voltage And Low Current Power Transformer
Get Best Deal

Dry Type Transformer - Customizable Specifications , Advanced Technology for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Get Best Deal
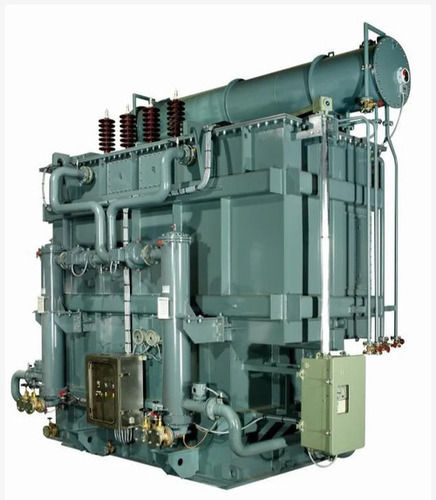

High-Efficiency Oil Immersion Transformer - 400 Kg Iron, 450 Volt High Voltage | 150 Kiloliter/Day Capacity, 99% Efficiency, Three-Phase Output
Price : 250000 INR
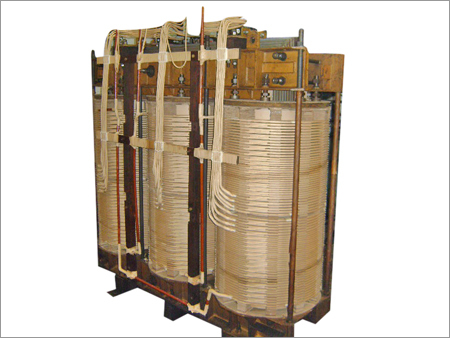
Power Transformer Assembly Coil Material: Copper Core
Price : 50000 INR
Isolation Transformers - High-Quality Components , Expert Manufacturing Compliance with Industrial Standards
MaterialCRGO steel
Dimensions300x200x150 cm
Weight1000kg
Power50kVA
Voltage415V
Frequency50 Hz
View More

Metal Domestic Isolation Transformers
Price : 42000 INR
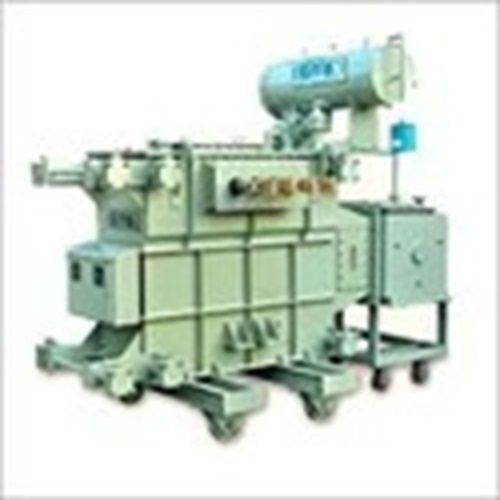

3-Phase 630 K Va Oltc Distribution Transformer
Price : 800000 INR
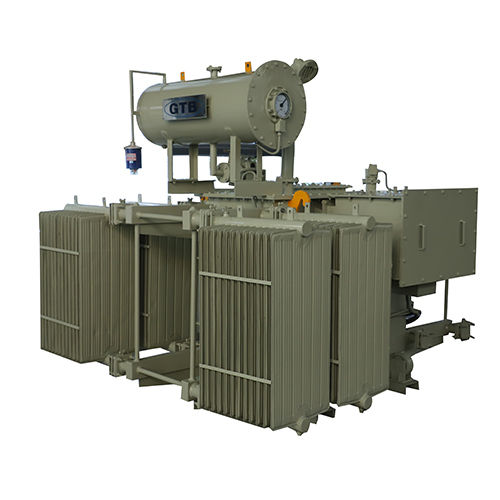

3150 Kva Transformer - Efficiency: High
Get Best Deal
Winding Machine For Motors And Transformers - Application: Industrial
Price: 90000 INR/Pack
MOQ1 Pack/Packs
ColorMulticolor
Product TypeElectronics Products
ApplicationIndustrial
SizeStandard
FunctionDigital
WarrantyYes
View More

Heat Transfer Lab Equipments - Application: Laboratory
Price Trend : 50000.00 - 500000.00 INR

Unsteady State Heat Transfer Apparatus - Application: Laboratory
Price Trend : 50000.00 - 500000.00 INR

Current And Voltage Transformers - Application: Industrial
Price Trend : 50000.00 - 500000.00 INR

Variable Three Phase Transformer - Application: Industrial
Price : 90000 INR
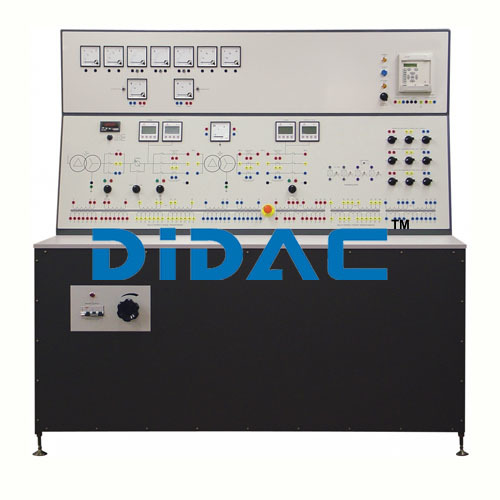

Transformer Trainer - Application: Industrial
Price Trend : 50000.00 - 500000.00 INR
2 In 1 Transformer Efficiency: 98%
Price: 40000 INR/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Cooling TypeOil & Air Cooled
Rated Voltage11000/433 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, transformer
Output415, 440V
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Efficiency98%
Reliable Power Systems
Faridabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller10 Years
View More

3-Phase 750 KVA Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer
Price : 900000 INR

Automatic Voltage Stabilizer - Application: Industrial
Price : 450000 INR
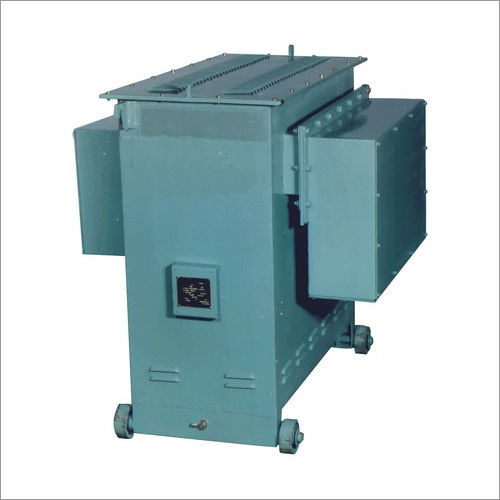

Industrial Voltage Controllers Efficiency: 98%
Price : 40000 INR

Voltage Regulating Transformer - Current Type: Ac
Price : 20000 USD ($)

High Frequency Isolation Transformer Efficiency: 98%
Price : 40000 INR

Industrial Furnace Transformer - Coil Material: Copper Core
Price : 40000 INR
Special Transformers - Customized High Voltage, Energy Industry Expertise | Quality Manufacturing, Expert Engineering
Power Rating1000 kVA
Voltage Range11 kV - 400 V
Frequency50 Hz
Cooling SystemONAN
Efficiency99%
MaterialCRGO Steel
Arihant Transformers
Indore
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller2 Years
View More
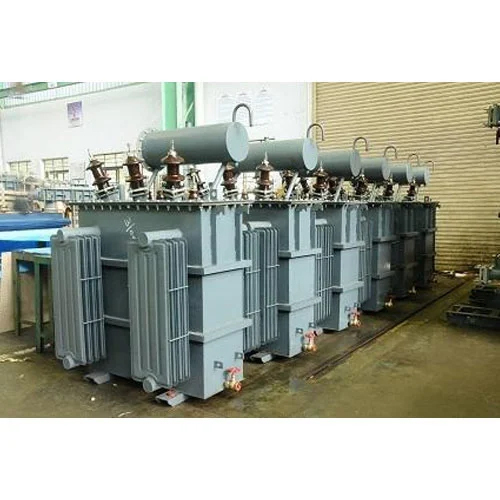

Distribution Transformers Testing Service
Get Best Deal

Top Performance Electrical Power Transformer
Get Best Deal
Distribution Transformers - Aluminum & Copper Windings, 10-1000 KVA Ratings, Customizable Specs for 3 Phase Networks
Core typeStacked
Rating10-1000 KVA
Voltage22-11 KV
WindingsAluminum/Copper
Phases3-Phase
CoolingNatural air
View More
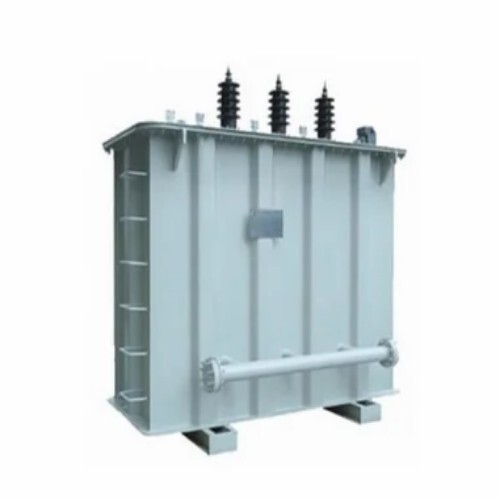

100Kva 3-Phase Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 10000000 INR

High Voltage Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 10000000 INR

Copper Wound Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 10000000 INR

Bis Approved Distribution Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 10000000 INR

1000Kva 3-Phase Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 10000000 INR
FAQs Related to Transformers - Ventilated Transformer Prices, Manufacturers & Suppliers
A transformer is
an electric gadget that transfers AC voltage from one level to another with the
least amount of energy loss possible. It is based on the electromagnetic
induction concept. A typical power transformer is made up of two coil sets:
primary and secondary. The number of turns on the main and secondary coils is
related to the rate of voltage transformation.
Transformers can
be operated at voltages lower than the nameplate rated voltage in some
instances. A transformer should never be run over its nameplate rating unless a
tap changer is available. When the voltage is lower than the rated voltage, the
KVA capacity is lowered accordingly.
The continual
expansion and contraction of the steel core inside the transformer causes
transformer hum or transformer noise. The quantity of flux determines core
expansion, which is determined by the applied voltage and the number of turns
in the transformer coils. The magnetic flux travelling through the transformer
core is constantly changing, causing the core to grow and shrink.
A power
transformer is mainly used in power transmission and distribution to either
step up or down a voltage level. In a circuit, an instrument transformer is
used to monitor voltage or current. Instrument transformers include current and
potential transformers, for instance.
The difference
between input and output power can be characterised as 'loss' in any electrical
equipment. Since an electrical transformer is a static device, it has no
mechanical losses (such as windage or friction losses). Simply electrical
losses make up a transformer (iron losses and copper losses). Transformer
losses are comparable to DC machine losses, with the exception that
transformers have no mechanical losses.
Distribution & Power Transformer
Product DescriptionBharti's Transformer are manufactured with standard rating & customer requirement, Bharti\342\200\231s Transformer are designed & tested as per IS2026. Our transformers are durable low capacitive, power saver and highly official.\015\012Product Range of Distribution & Power Transformer:\015\0121.Upt
Bharti Engineers
Ludhiana
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller19 Years
View More
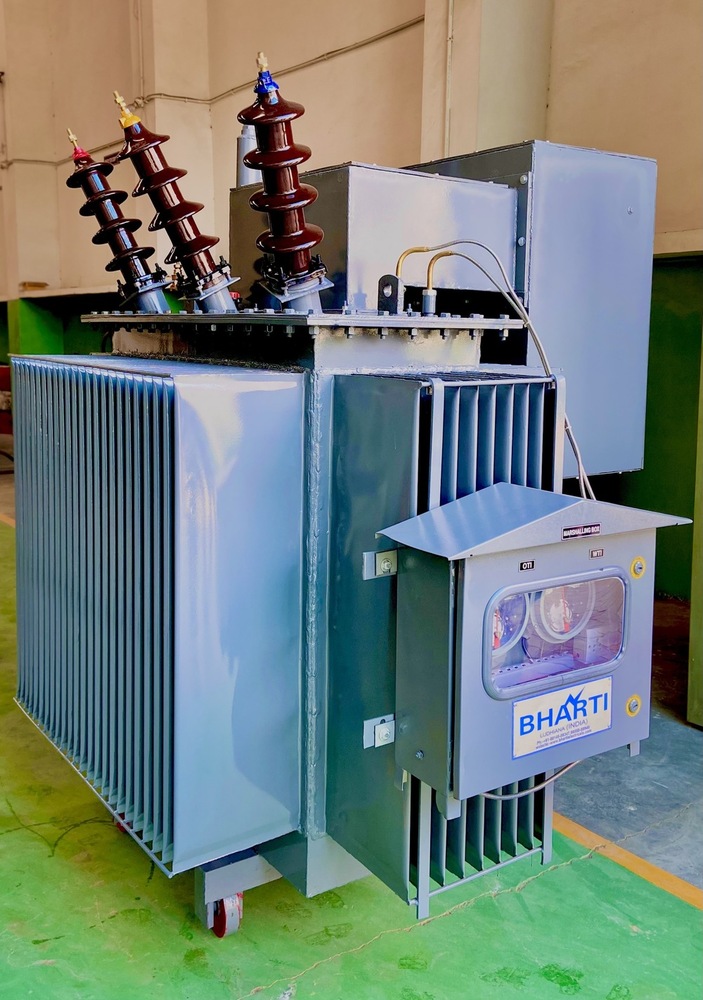

Furnace Transformer - Capacity: 500Kva Pcs/Min
Price : 890000 INR
500 Kva Transformer
KVA500
Voltage11000/433V
CoolingOil cooled
WindingCopper
Tap changerOn-load
ConnectionDelta/Star
View More
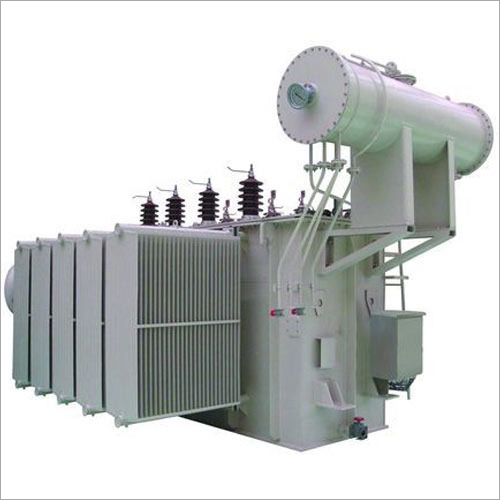

Distribution Transformer Rental Service - 11000V HT Dry Type, >100 KVA Capacity | Customized for Temporary Power Solutions in Manufacturing and Large Projects
Price : 300000 INR

Transformer Repair Service
Price Trend : 45000.00 - 60000.00 INR

Dry Type Transformers - Capacity: 100 Kg/Hr
Price : 200000 INR
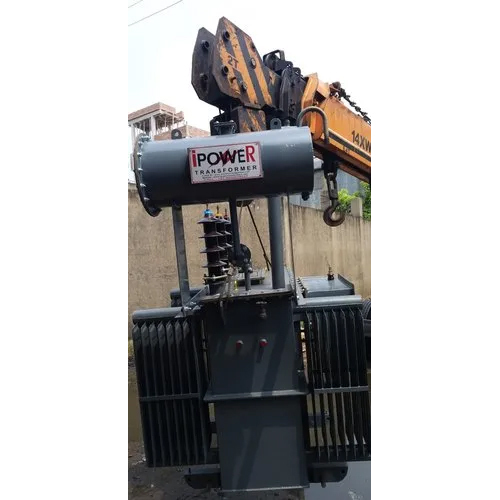

500 Kva Power Distribution Transformer - Material: Copper
Price : 665000 INR
Step Up Transformer - 100 Watt Maximum Capacity | Durable Design for Continuous Usage, Fault-Free Performance
Power Output100W
Input VoltageRange 120-240V
Output VoltageRange 220-480V
Efficiency85-90%
Weight10-20kg
Dimensions30x40x50cm
Servostar India Private Limited
Ghaziabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller11 Years
View More

Buck Boost Transformer - Premium Quality Components, Customized Specifications for Servo Stabilizers
Get Best Deal
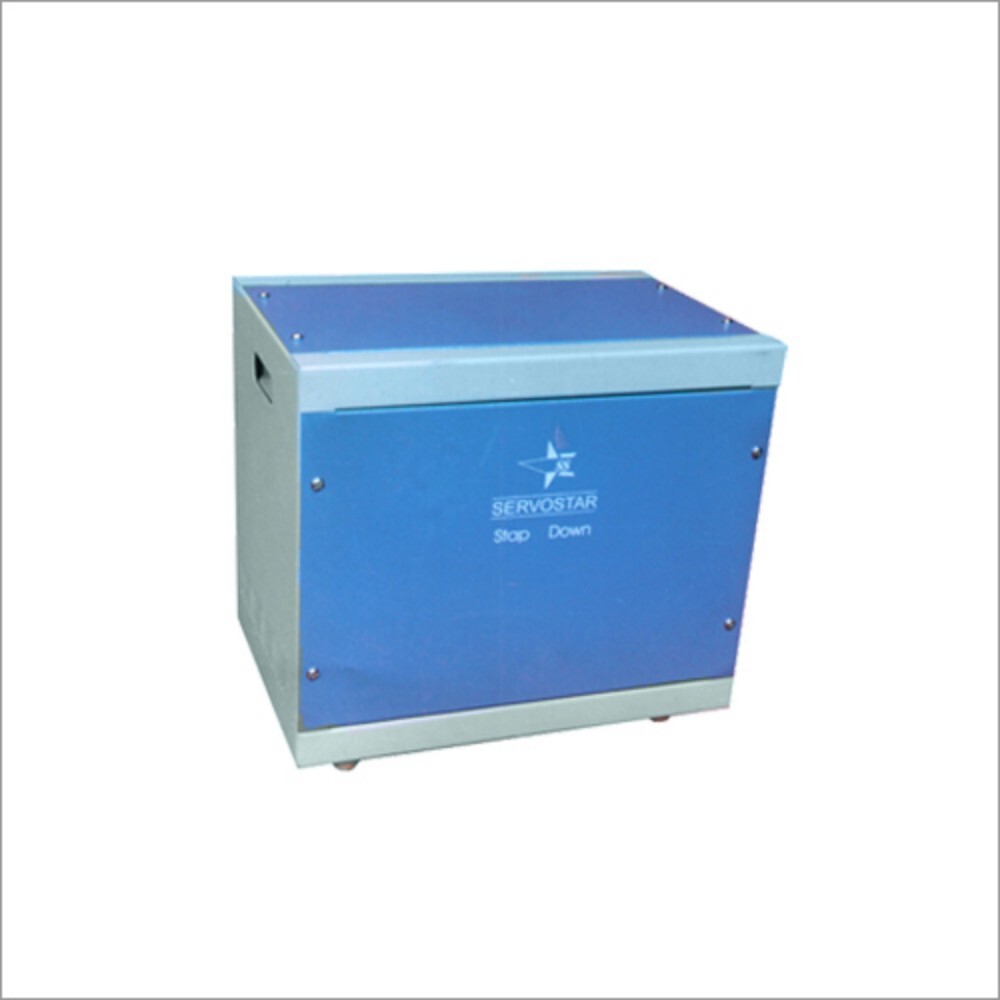

Step Down Transformer - Material: Stainless Steel
Price : 9000 INR
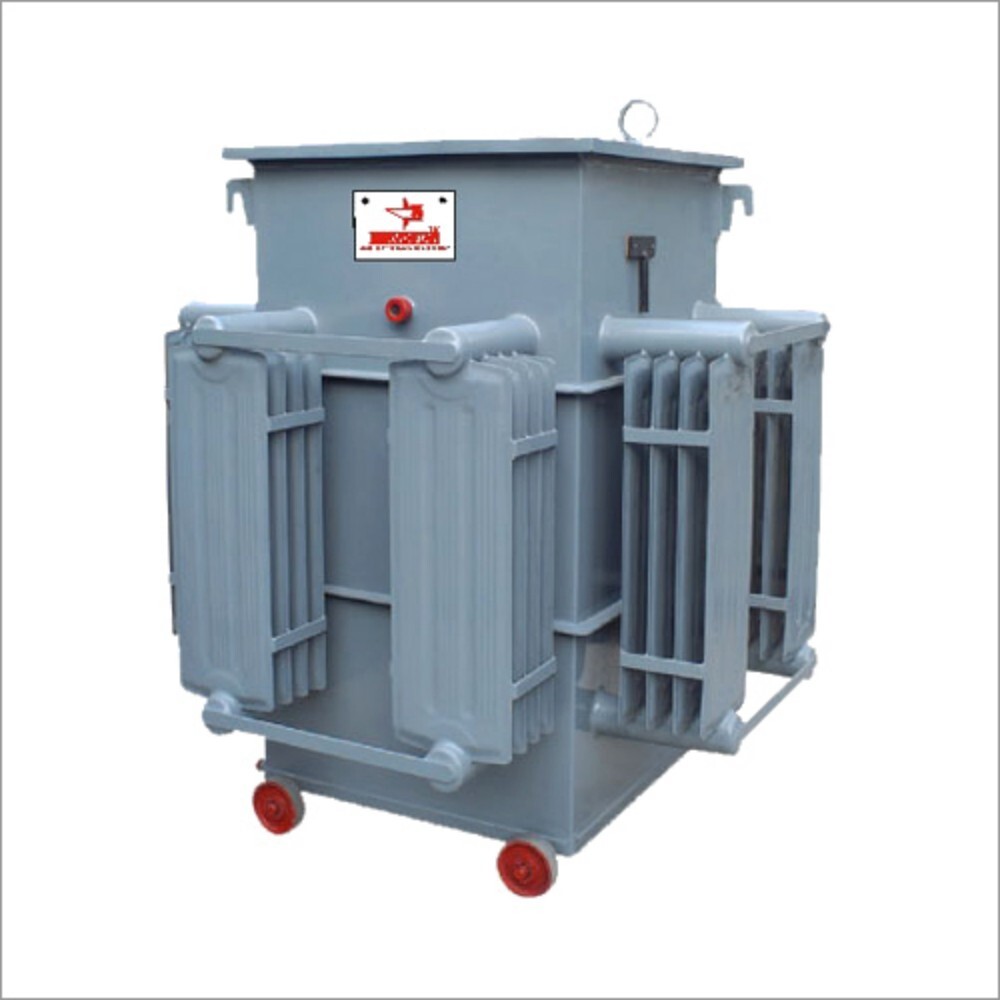

Ultra Isolation Transformer - Material: Stainless Steel
Price : 115000 INR

Isolation & Ultra Isolation Transformer
Get Best Deal
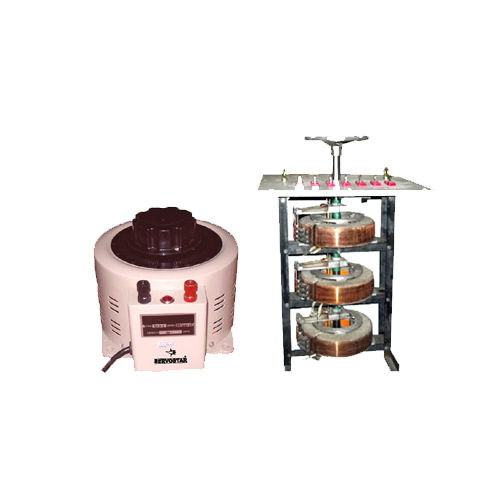

Mild Steel Auto Variable Transformers Variac
Price : 8000 INR
Transformers - Optimized Performance with Three Phase & Single Phase Designs | Special Transformers, Power Transformers, Servo Voltage Stabilizers, and Lighting Arresters
Product TypePower Transformer
Primary ColorGray
Power Rating10-1000 kVA
Voltage Range100-66kV
Frequency50/60 Hz
Efficiency98%
Transcon Industries
Hyderabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller8 Years
View More
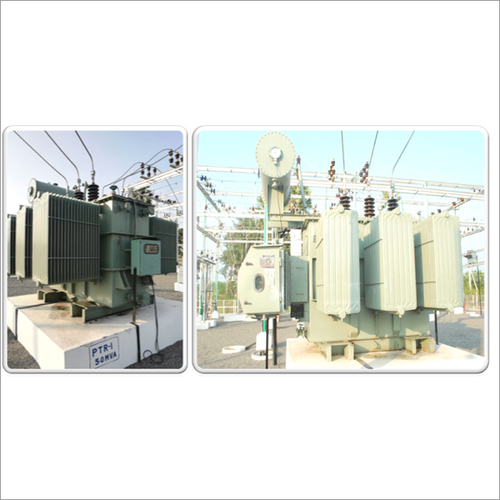

Copper wound OLTC POWER Transfromers
Price : 550000 INR
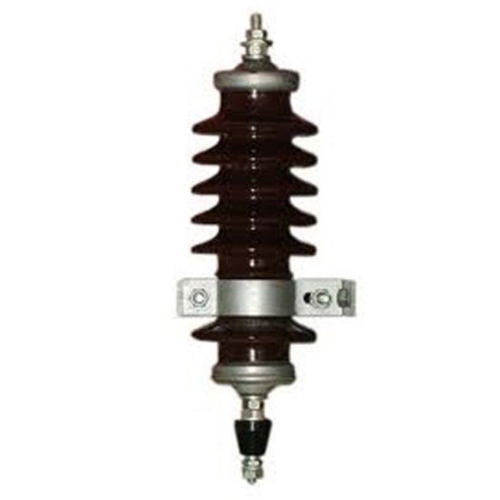

Lighting Arrestors
Price : 17500 INR
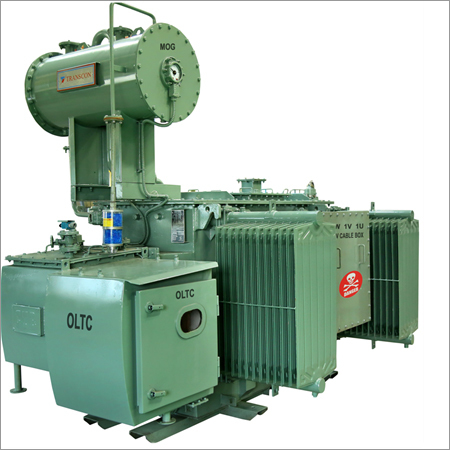

Three Phase Distribution Transformers Up to 2.5 MVA as per IS 1180
Price : 959000 INR
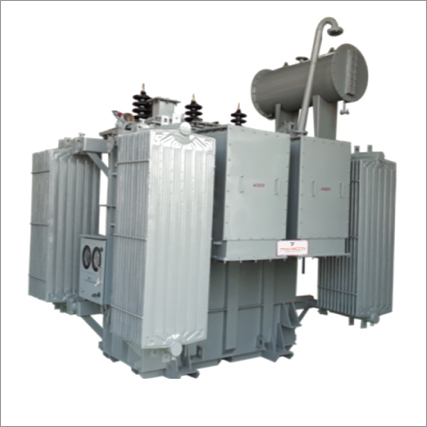

Solar Inverter Transformers
Price : 400000 INR
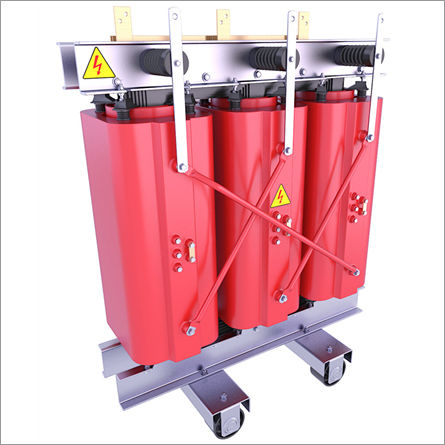

Cast Resin Dry Type Transformers
Price : 550000 INR
Single Phase Transformer - Copper Wound, 5kVA Rated Power | Efficient Energy Conversion, Compact Design, Reliable Performance
Cooling TypeAir Cooled / Oil Cooled
High VoltageUp to 11000 V
Coil MaterialOther , High Grade Copper
Load Loss<1% of Total Load
Dimension (L*W*H)Approx. 400 x 300 x 350 mm
Voltage Booster TypeOther, Auto and Isolated Transformer Types
View More

300kVA 3-Phase Transformer
Get Best Deal
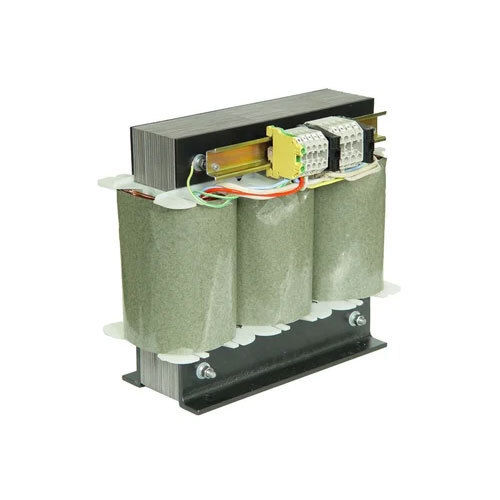

100kVA 3-Phase Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer
Get Best Deal
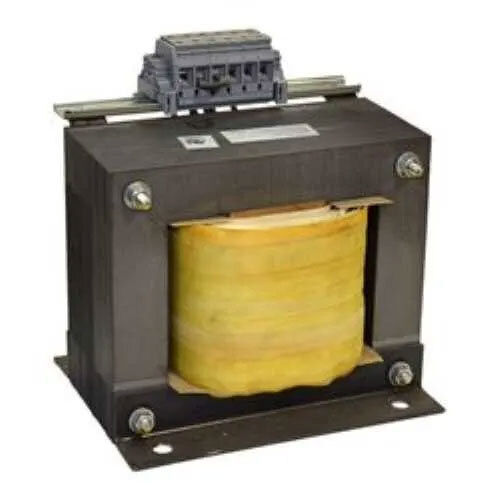

1kVA Single Phase Isolation Transformer
Get Best Deal
New Transformers - Features: Premium Quality
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Voltage Booster TypeDry
MaterialMild steel
PhaseThree Phase
UsageIndustrial
Warranty1 Year
FeaturesPremium quality
Trishul Engineering Co.
Ghaziabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller3 Years
View More
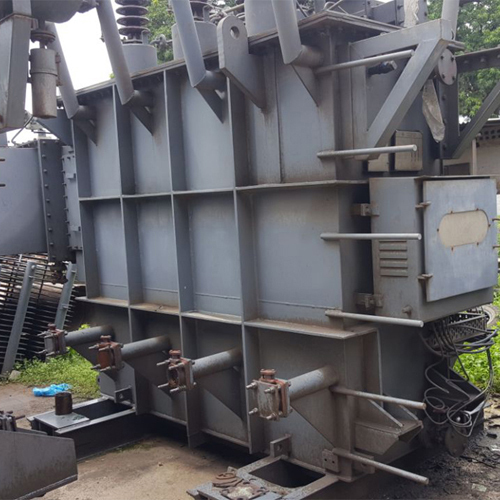

Kirloskar Make 750 Kva 11-433 Oltc Type Transformer - Features: Premium Quality
Price : 500000.0 INR
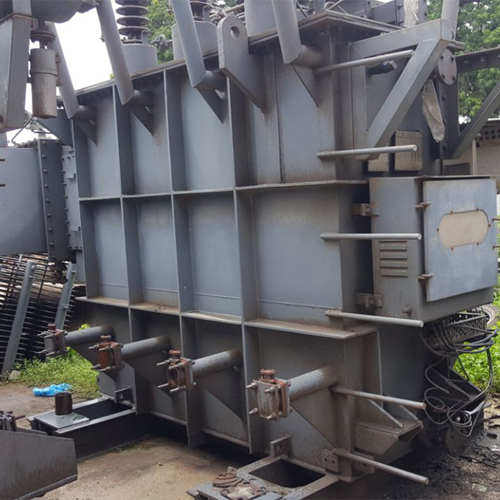

Crompton 1000 Kva 11-433 Offload Type Transformer - Features: Premium Quality
Price : 1050000.0 INR

Siemens Electrical Power Transformer - Features: High Quality
Price : 400000.0 INR
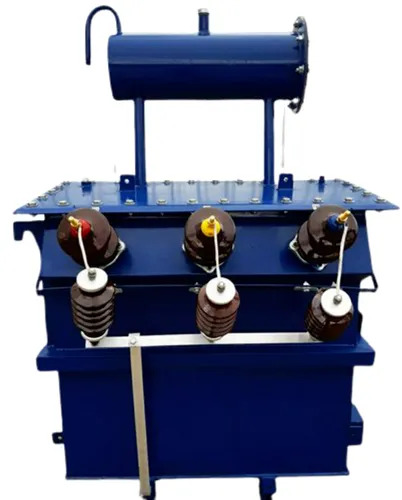

100 Kva Oil Cooled Distribution Transformer - Features: Good Quality
Price : 100000 INR
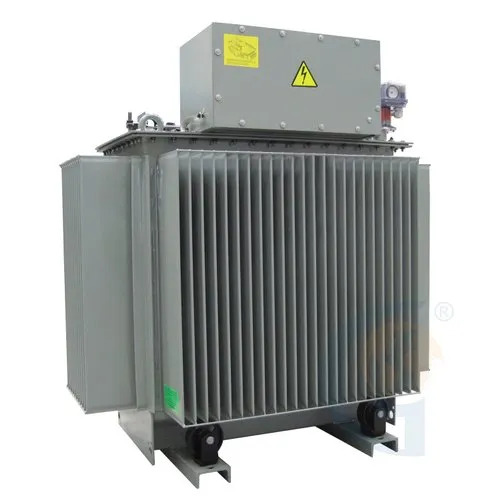

Three Phase Distribution Transformers - Features: High Quality
Price : 200000 INR
2mva Transformer
Product DescriptionWe offer our client an excellent quality range of 2MVA Transformers, which are manufactured from high grade quality raw materials. These 2MVA Transformers can be customized as per our precious customers specifications. These 2MVA Transformers are widely known for its durability and quality. Our 2MVA
View More
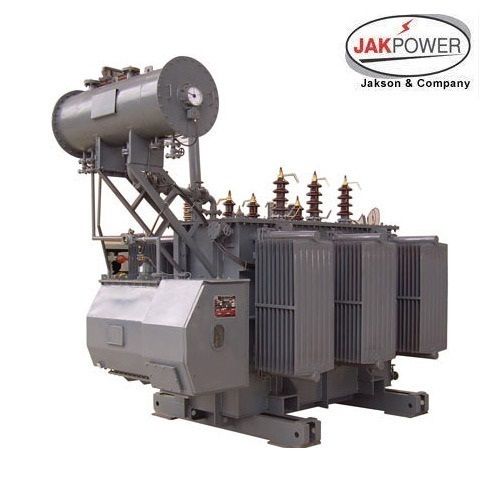

High Power Transformers - Efficiency: 97%
Get Best Deal

500kva, 110/43 Oil Cooled Transformer
Get Best Deal
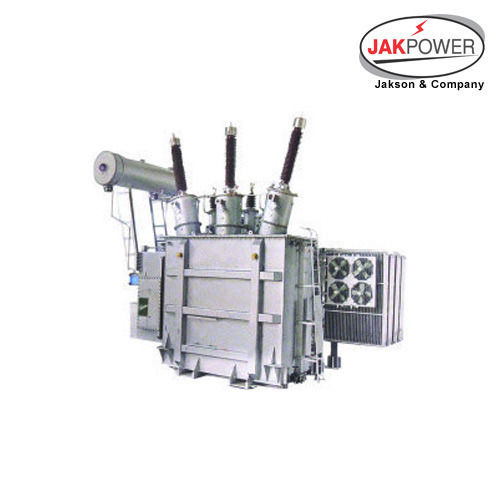

Power Transformers - Efficiency: 97%
Get Best Deal
1KVa Transformer
Load LossNot specified in the image
Coil MaterialOther , Copper
Dimension (L*W*H)Not specified in the image
Operating TemperatureNot specified in the image
Cooling TypeAir cooled
Capacity1KVa
Ambala Electronic Instruments
Ambala Cantt
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller11 Years
View More
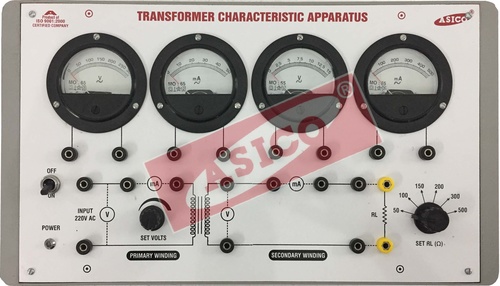
Transformer characteristics Apparatus
Get Best Deal
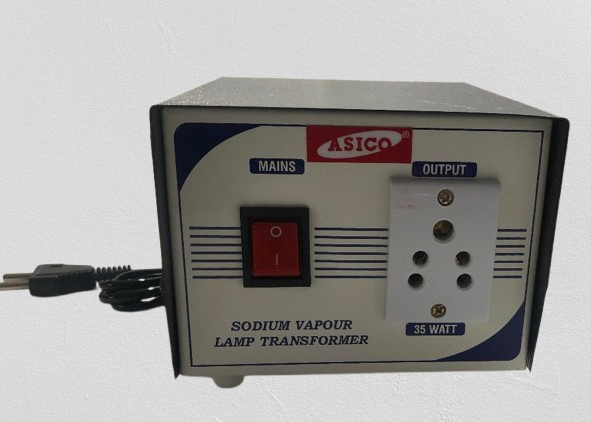

Sodium Vapor Lamp Transformer
Get Best Deal
Heavy Duty Transformers - High Grade Raw Materials | Durable, Customizable, Excellent Quality Range
Power Rating1000 kVA
Voltage11 kV
Frequency50 Hz
Efficiency98%
CoolingONAN
MaterialCRGO Steel
View More
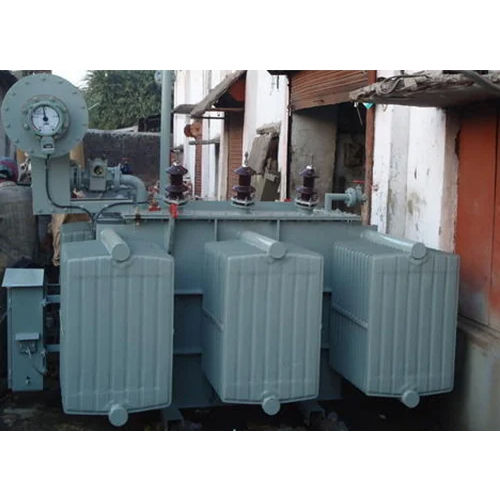

1500 Kva Distribution Transformer - Frequency (Mhz): 50-60 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 2000000 INR
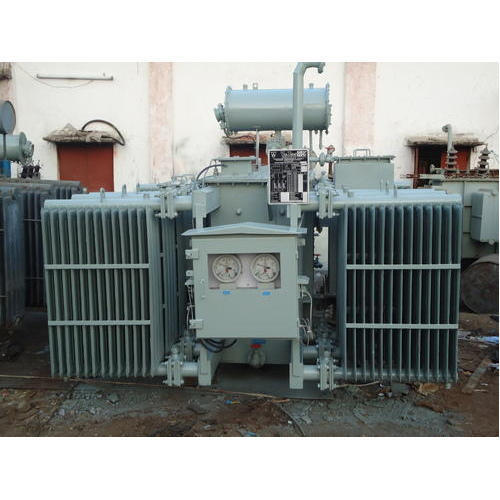

2000 KVA Transformer
Get Best Deal

Alloy 250 Kva Dry Type Transformers
Get Best Deal
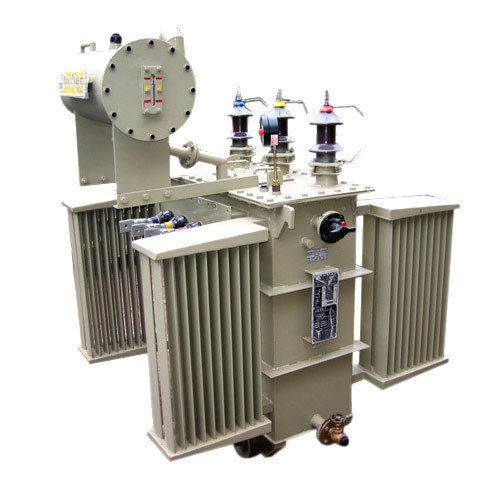

Three Phase Lt Transformer
Price : 500000.0 INR
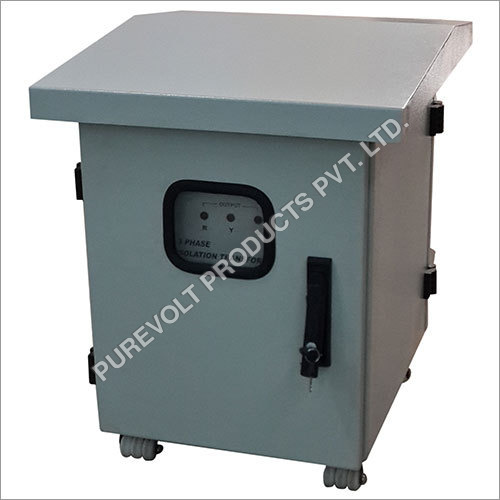
Ferro Resonant Transformer Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price: 4000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Cooling TypeAir Cooled and Oil Cooled
Rated Voltage220-440 Volt (V)
Product TypeElectrical Transformer
MaterialMetal
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Power ScopeElectric
Purevolt Products Pvt. Ltd.
New Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller12 Years
View More

E I Transformer - Metal, 110-690 Volt Rated Voltage | Lightweight, High Performance, Long Lifespan, Faultless Quality, Short Circuit Tolerant
Price : 2000 INR

Manual Variable Auto Transformer Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 4000 INR

3 Phase Isolation Transformer Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 15000 INR

Variable Auto Autotransformer Frequency (Mhz): 50-60 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 4000 INR
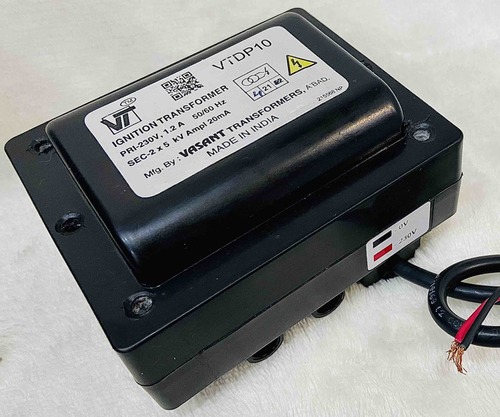
Ignition Transformers(Oil/Gas) Vtdp10/Vtsp10 Frequency (Mhz): 50-60 Hertz (Hz)
Price: 1300 INR/Piece
MOQ10 Piece/Pieces
Rated Voltage230 Volt (V)
Product TypeOther, Ignition Transformers
MaterialPlastic
Frequency (MHz)50-60 Hertz (HZ)
UsageIndustrial
Weight1-10 Kilograms (kg)
View More
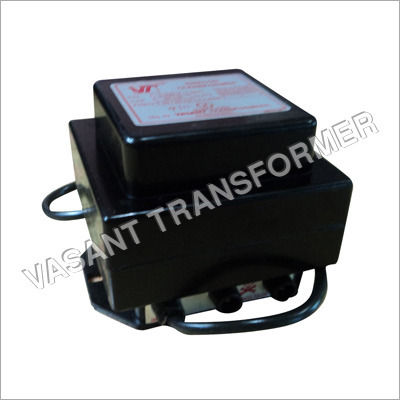

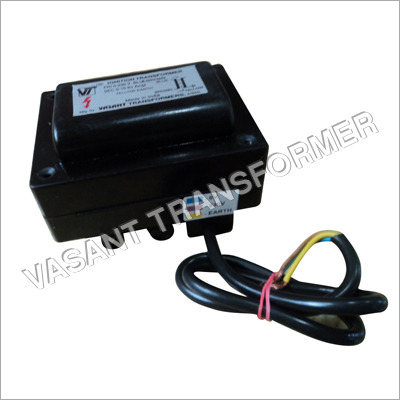
Ignition Transformer (Vtsp12,Vtdp12)
Price : 1600.00 INR

Static Eliminator Transformers
Get Best Deal
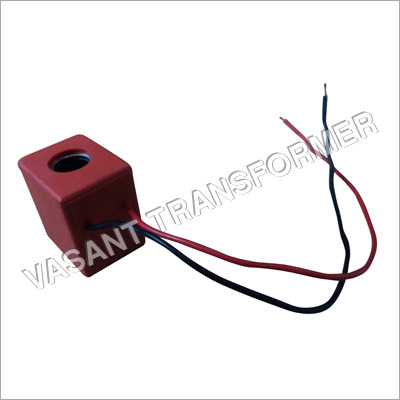

Hydraulic Solenoid Coils Application: For Industrial Use
Price : 150-200 INR
IGBT Transformer
MaterialHigh-grade steel
Dimensions10x10x5cm
Weight1kg
Power rating1KW
InsulationClass F
Frequency50/60Hz
View More

Ram Piston Type Briquetting Machine Transformer
Get Best Deal

Electric UI Core
Get Best Deal

Industrial Toroidal Core
Price : 75 INR

Electrical Lamination Core
Get Best Deal
Sensing Transformers
MaterialFerrite Core
Dimensions4x4x3 cm
Weight150g
Terminals8 Pins
Frequency50-60Hz
Accuracy+/-1%
View More
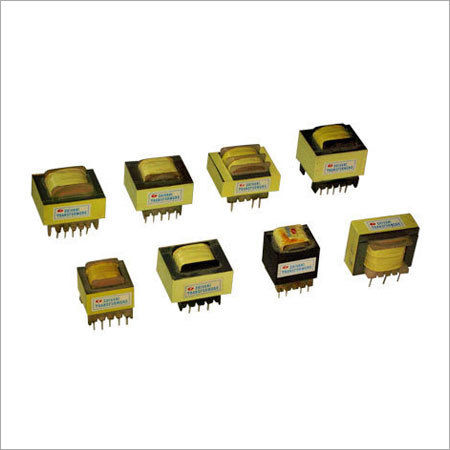

Pulse Transformers - Customizable Precision Engineering | Industry Standard Compliance, Tailored Modifications
Get Best Deal
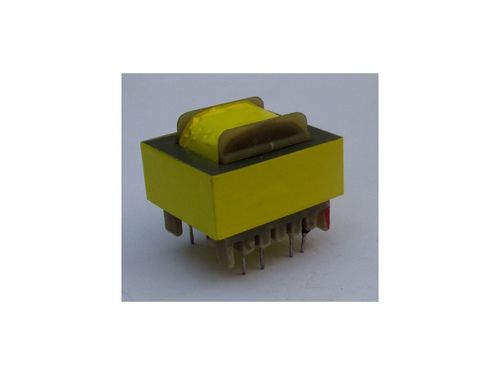
Sensing Transformer - 50-60 Hertz Frequency, Single Phase, 220 Volt Rated Voltage | 500 Grams Lightweight Design
Price : 150 INR

High Frequency Transformers - Features: Good Quality
Price : 500 INR
Portable Closed Auto Transformer - PVC Material, 420 Grams Weight | Rugged Build, High Efficiency, Smooth Output, Low Maintenance
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeTransformers
MaterialPVC
Measuring Voltage Range1 - 200%
Colorwhite
Weight420; 360 Grams (g)
View More

White Single Phase Transformer
Get Best Deal

Current Transformer - High Permeability Silicon Steel, Compact Design with Sturdy Built and Economical Performance
Get Best Deal

Transformers Ac/Dc Motors
Price : 10000 INR

Three Phase Transformer - Color: White
Price : 8000.00 INR

Black Current Transformers
Get Best Deal
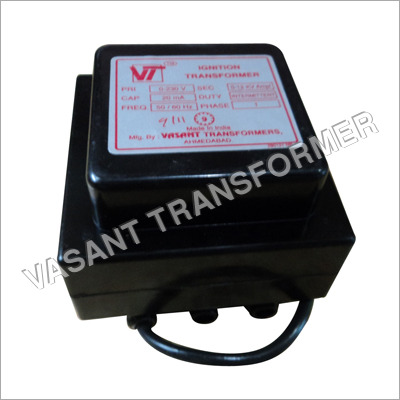
Ignition Transformer - Color: Black
Price: 2000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeIgnition Transformer
ColorBlack
ConditionNew
TypeNatural Circulation
UsageIndustrial
StructureFire Tube
View More

Heavy Duty Burner - Color: Red And Black
Price : 35000.00 INR
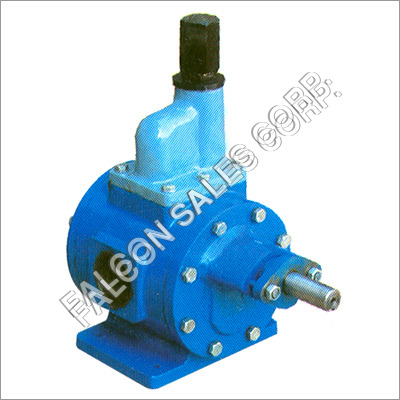

External Gear Pump - Cast Iron, High Pressure, Electric Powered | Self-Priming, Compact Design, Dual Rotating Parts, Leak-Proof Performance, Versatile Applications in Industry
Price Trend : 2000.00 - 5000.00 INR

Burner Control Box - Color: Black And White
Price Trend : 2500.00 - 4200.00 INR

Automatic Gas Burner - Color: Red And Black
Price : 58000.00 INR
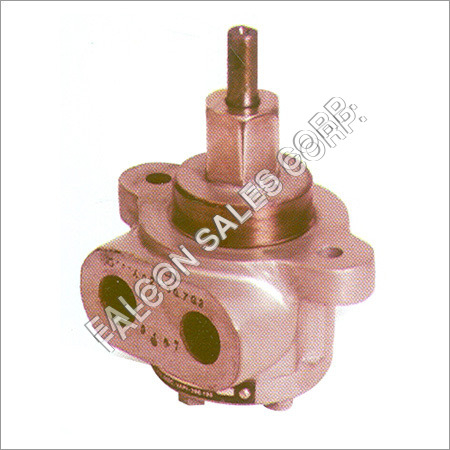

Cast Iron Prakash Gear Pumps
Price Trend : 2000.00 - 4000.00 INR
Copper Transformer Capacity: 125% For 10Mins
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Coil MaterialCopper Core
High Voltage415 Volt (V)
Rated Voltage295V aEUR" 470V Volt (V)
Cooling TypeAir Cool
Capacity125% for 10Mins, 150%for 1Sec. Kg/day
Low Voltage230 Volt (V)
View More

3 Phase 250Kva Isolation Transformer Frequency (Mhz): 50 Hertz (Hz)
Price : 485000 INR
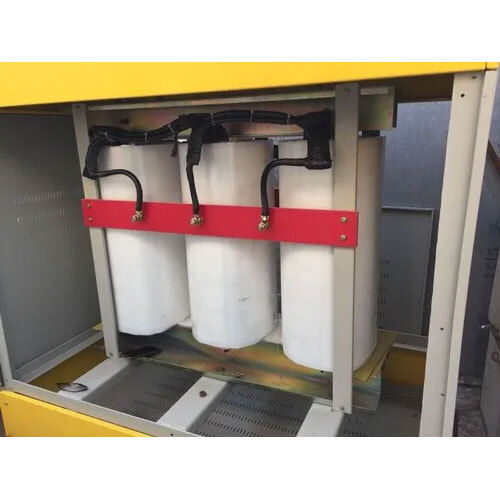

Xtaton Isolation Transformer Phase: Three Phase
Price : 68000 INR
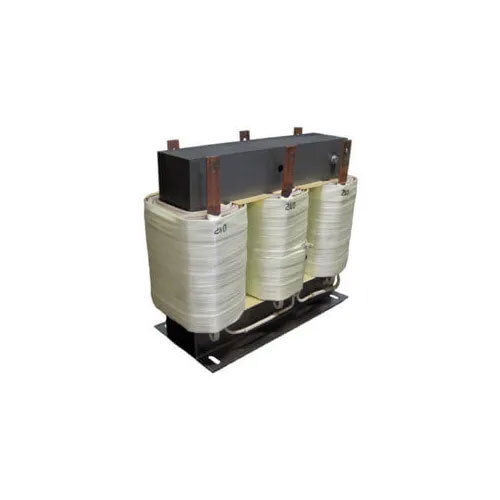

Ultra Isolation Transformer - Copper Material, Three Phase, Oil Cooled | Designed for Industrial Applications
Price : 55000 INR
Popular Transformers - Ventilated Transformer Prices, Manufacturers & Suppliers
A transformer is a
device that converts electrical energy from one circuit to another, or several
circuits. A changing current in any transformer coil causes a changing magnetic
flux in the core, which causes a changing electromotive force across all other
coils coiled around the same core. Without the need for a metallic link between
the two circuits, electrical energy can always be exchanged between them.
Depending on its
end-use, construction, supply, and function, electrical transformers can be
divided into several types. Based on the design, there are two types of
transformers: core type transformers and shell-type transformers. On the basis
of supply, there are two types of transformers: single-phase transformer and
three-phase transformer.
On the basis of
purpose, there are two types of transformers: step up transformer and step-down
transformer. Whereas on the basis of use, there are three types of
transformers: power transformer, distribution transformer and instrument
transformer. On the basis of cooling, there are three types of transformers:
self-cooled oil-filled transformers, water-cooled oil-filled transformers and
air-cooled (air blast) transformers.
Transformers are
used in electric power transmission to allow high-voltage transmission, which
lowers the loss caused by wire heating. This makes it possible to put producing
units at a cost-effective distance from electricity users. By the time it
reaches the customer, almost all of the world's electrical power has travelled
through a succession of transformers. A transformer is used in many electronic
equipments to convert voltage from distribution cable to useful values for
circuit requirements, usually immediately at the power line frequency or via a
switch mode power supply.
Sellers at Tradeindia are dealing in advanced technology Transformers for meeting the demands of transmission line application. For all their products requirements they can reach out to us through email or SMS. Our team will provide prompt response to all their queries.
Related Blog Topic:
Top 10 Best Transformers Manufacturers, Suppliers & Exporters in India
Client Testimonials & Reviews

GangaramPatel
APEX ELECTRICALS
We have been associated with Tradeindia, since more than a year and we feel happy to say that their services have been excellent during our courtship and has become our effective marketing tool to explore the Domestic and International market. We wish to continue with their improving services in years to come. All the best for Tradeindia team.

AnoopGupta
PRADEEP SALES & SERVICE PRIVATE LIMITED
We are greatly satisfied with your timely response. Thank you for the prompt response in intimating the queries.
Transformers - Ventilated Transformer Prices, Manufacturers & Suppliers Price List
Product Name | Expected Price |
|---|---|
| Auto Transformers | 50000 |
| Control Transformers | 4200 |
| Transformers | 10000 |
| Step Down Transformers | 400000 |
| Hermetically Sealed Transformers | 230000 |
| ETD 3920 24V PCU SMPS Transformer | 95 |
| Power Transformer | 950000 |
| Earthing Transformers | 250000 |
| 250 Kva Transformer | 255000 |
| Step Up Trasformer | 40000 |
This Data was Last Updated on 2025-12-24
Transformers - Ventilated Transformer Prices, Manufacturers & Suppliers Manufacturers | Suppliers in India
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Bharti Engineers Ludhiana, India | 19 Years |
Kunal Stamping Pvt. Ltd. Delhi, India | 19 Years |
Hindustan Power Products (p) Ltd. Jhajjar, India | 18 Years |
Urja Techniques (india) Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai, India | 18 Years |
Thermocool Engineering Pvt Ltd Kolkata, India | 18 Years |
Shivani Transformers New Delhi, India | 18 Years |
Jakson & Company New Delhi, India | 17 Years |
Falcon Sales New Delhi, India | 16 Years |
Futuristic Technologies Ahmedabad, India | 15 Years |
Vasant Transformers Ahmedabad, India | 15 Years |
Upcoming Tradeshows
CWIEME Shanghai 2026
Wed, 24 Jun, 2026 - Fri, 26 Jun, 2026
INDOMACH Jamshedpur 2026
Thu, 05 Feb, 2026 - Sun, 08 Feb, 2026
Asia Photonics Expo (APE 2026)
Wed, 04 Feb, 2026 - Fri, 06 Feb, 2026
IFF - India Fashion Forum 2026
Wed, 28 Jan, 2026 - Thu, 29 Jan, 2026
Plastic Packaging Printing Expo (P3) 2026
Fri, 10 Apr, 2026 - Mon, 13 Apr, 2026
STEEL CONSTRUCTION EXPO 2026
Thu, 26 Feb, 2026 - Sat, 28 Feb, 2026
Panacea - Natural Products Expo India 2026
Fri, 06 Mar, 2026 - Sun, 08 Mar, 2026
India Boat & Marine Show 2026
Thu, 29 Jan, 2026 - Sat, 31 Jan, 2026
Spectra Expo 2026
Wed, 06 May, 2026 - Fri, 08 May, 2026
Odisha Mining & Infrastructure International Expo 2026
Thu, 08 Jan, 2026 - Sun, 11 Jan, 2026
Popular Categories