- Tradeindia
- Medical Equipment
- Mri Machine
Mri Machine
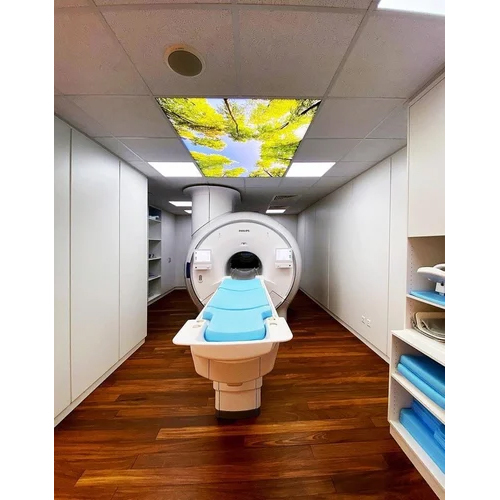
(249 products)Advanced Open MRI Machine - Polypropylene Material, 440 Volt Power Source | Automatic Operation, Digital Display, 1 Year Warranty
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Automation GradeAutomatic
ConditionNew
UseHospital
Warranty1 Year
MaterialPolypropylene
Voltage440 Volt (v)
View More
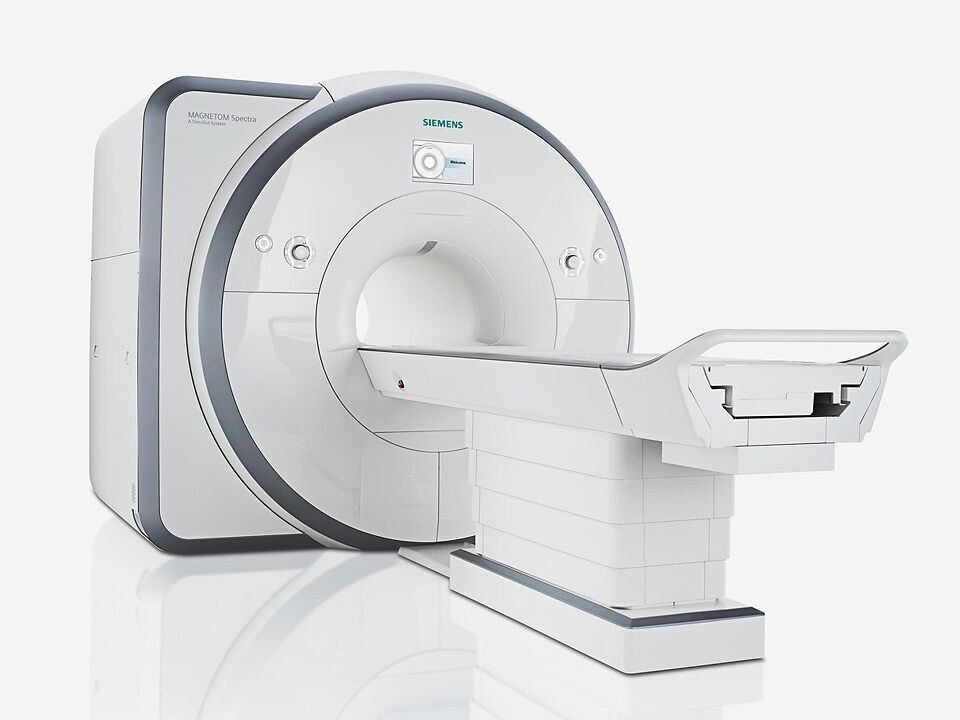
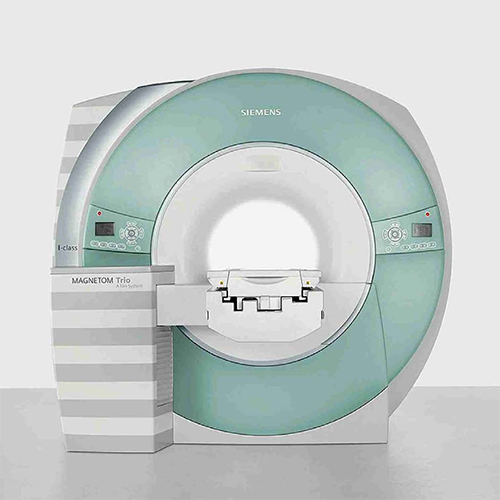
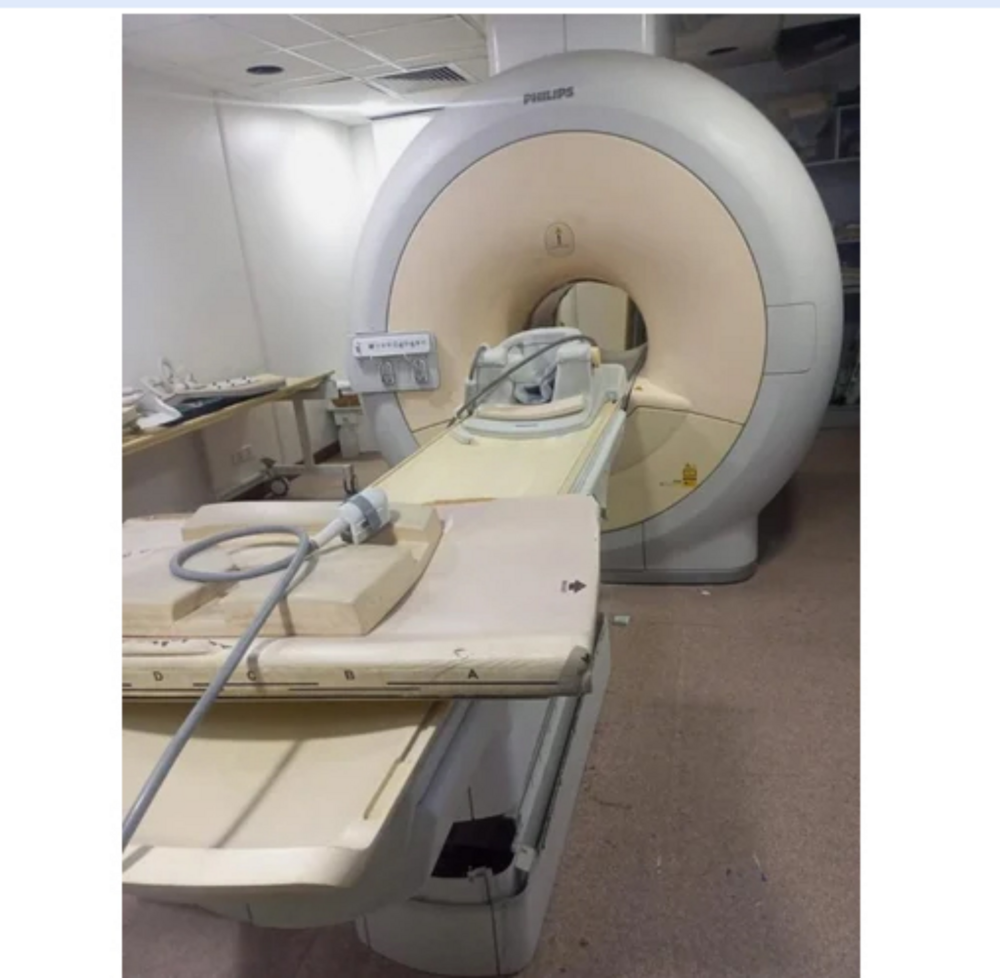
Siemens Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Get Best Deal
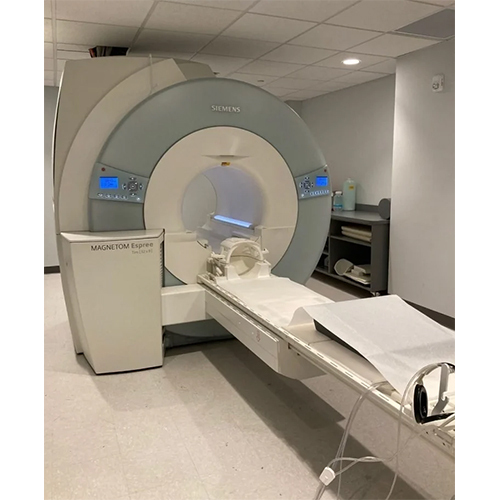
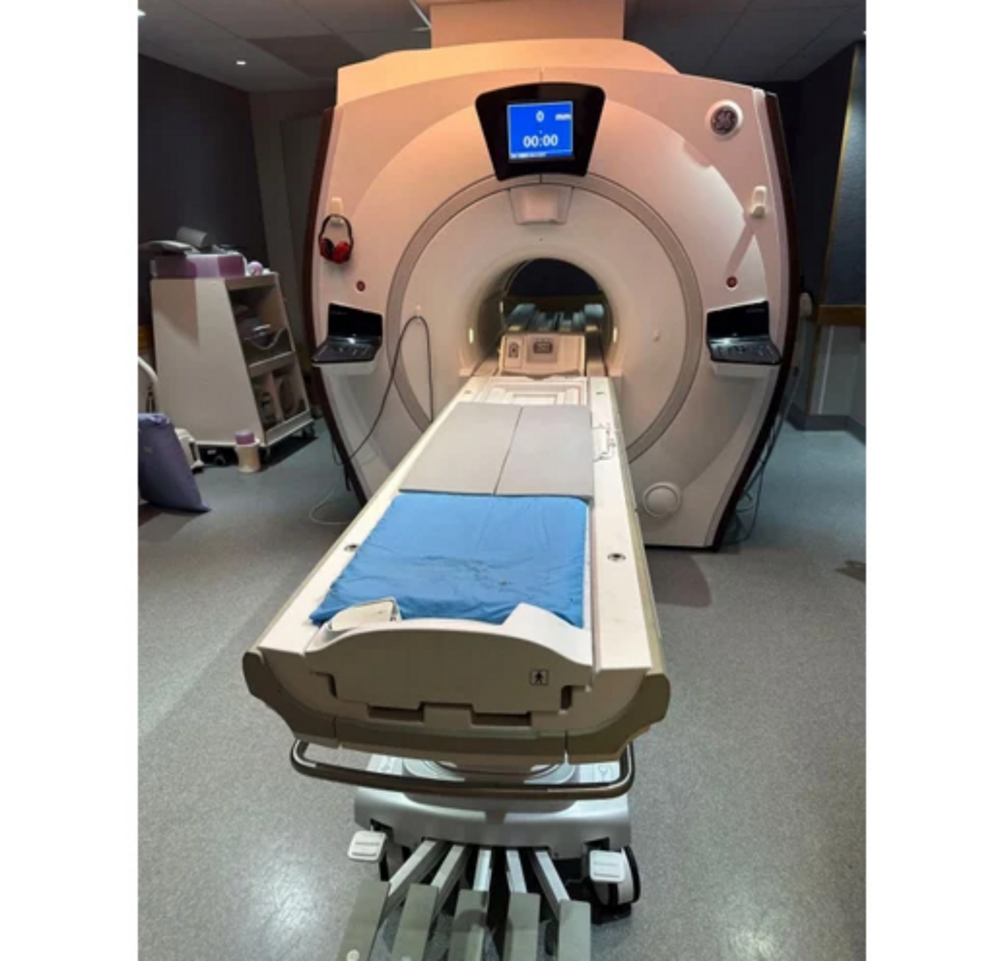
Open Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Get Best Deal
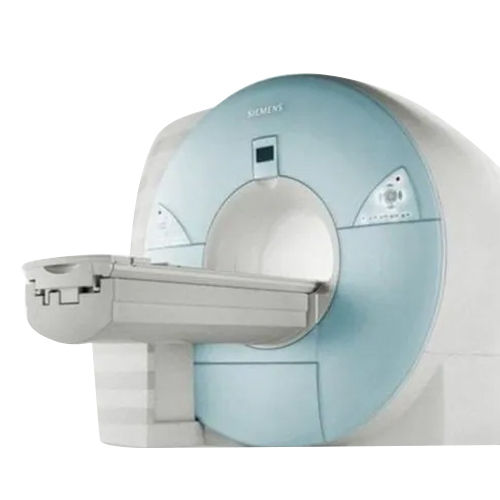
Refurbished Ge 1.5T Explorer With 25X Software Mri Machine - Color Code: White
Price: 35000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Color CodeWhite
Product TypeRefurbished GE 1.5T Explorer with 25x Software MRI Machine
Materialsuperconducting electromagnets, copper, aluminum, epoxy, plastic, and titanium
Suitable ForMRI
UseHospital
Power220 Volt (v)
A.K. Anthem Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.
Noida
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Super Seller
Super Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller1 Years
View More
Refurbished Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5T Mri Machine - Color Code: White
Price : 27500000 INR
GE 1.5T Creator MRI Machine - Superconducting Electromagnets, Customized Dimensions, Sleek White Finish | High-Resolution Diagnostic Imaging for Hospitals
Price : 40000000 INR
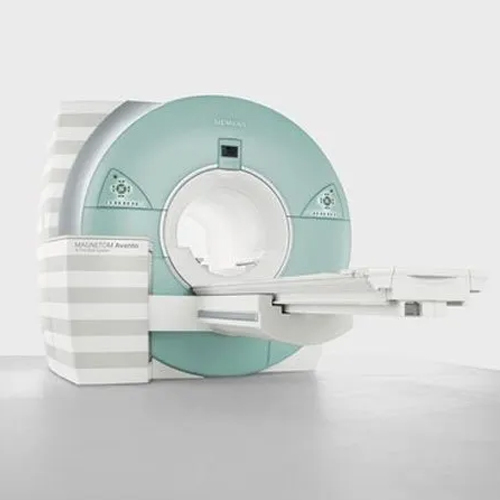
Refurbished Siemens Mri Scan Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 28500000 INR

Ge 1.5T Hdxt Mri Scanners Machine - Color Code: White
Price : 28500000 INR
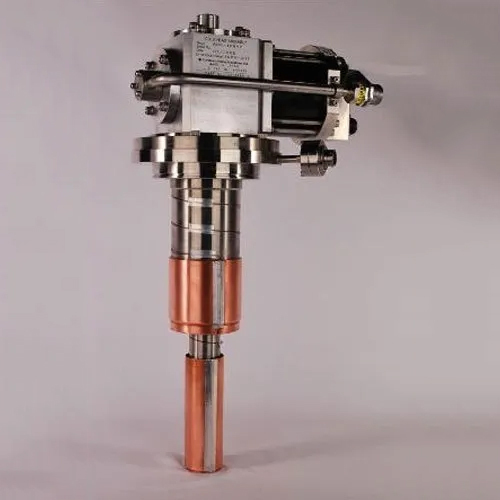

Sumitomo Rdk 408A3 Ge Mri Coldhead Machine - Dimension (L*W*H): 32 Inch (Width) Inch (In)
Price : 850000 INR
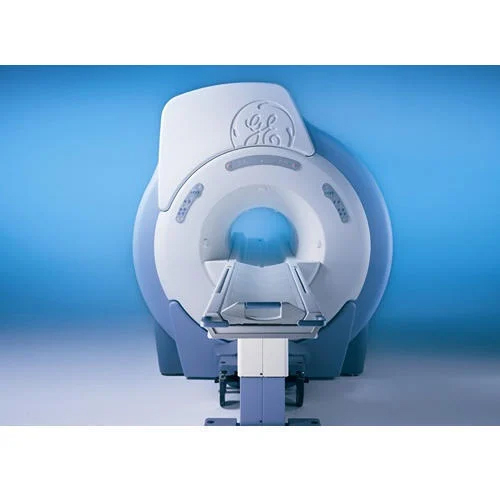
Refurbished Ge Signa Excite Echospeed Plus 1.5T Mri Machine - Color Code: White
Price : 21500000 INR
Ge Hdxt 1.5T Mri System - Application: Commercial
Price: 25000000.0 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
UseMedical
PropertiesHigh Quality
Product TypeCT Scan Machine
MaterialStainless Steel / PVC
Suitable ForMedical Labs / Hospital
ApplicationCommercial
Refurbished Siemens 3T Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
MOQ1 Unit/Units
MaterialPolypropylene
ConditionNew
ColorWhite
Automation GradeAutomatic
Warranty1 Year
UseHospital
Mevian Technology Private Limited
Secunderabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller1 Years
View More

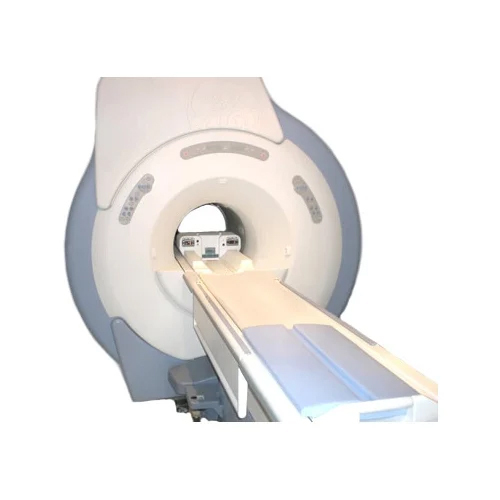
Siemens Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Get Best Deal

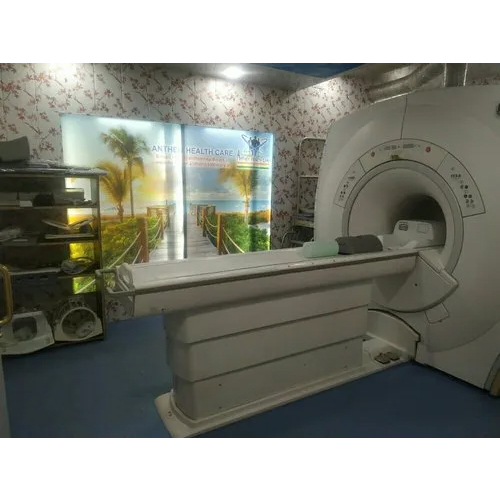
Open Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Get Best Deal
Mri Scanner - Application: Hospital
Price: 8499998.0 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeMedical Equipment
MaterialPlastic
UseMRI
Color CodeWhite
Weight1500 Kilograms (kg)
ApplicationHospital
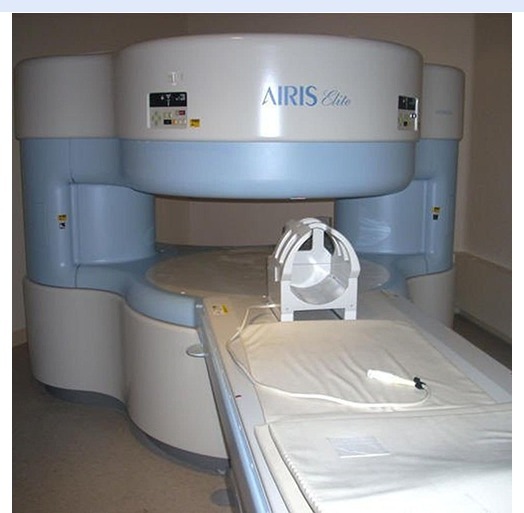
Airis Elite 0.3 Tesla - Accuracy: 100 %
Price: 150000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Sizeas for costumer
ConditionNew
Accuracy100 %
Functionnil
Automation GradeAutomatic
AttributesHigh Quality
View More
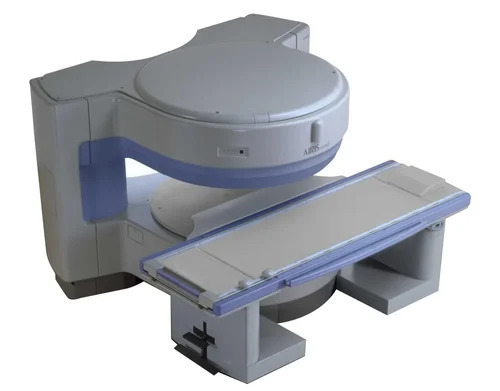
Hitachi Airis Mate Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 6000000 INR
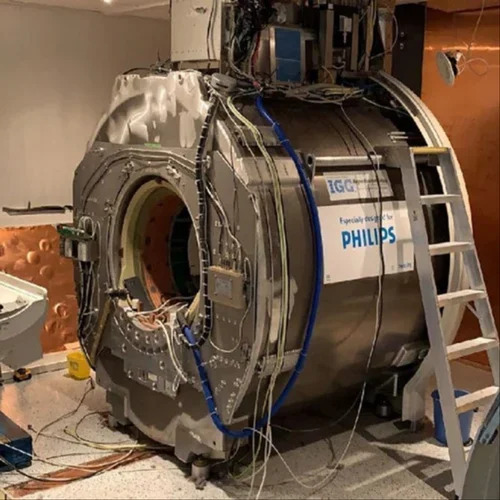

Mri Machine Repairing Service
Price : 25000 INR
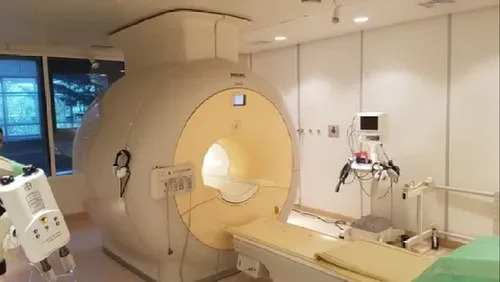
Philips Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 22500000 INR
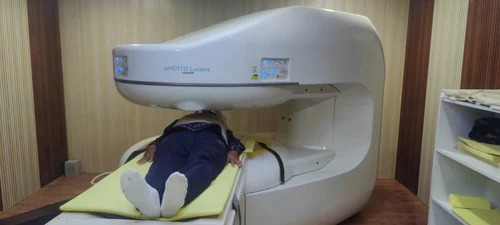
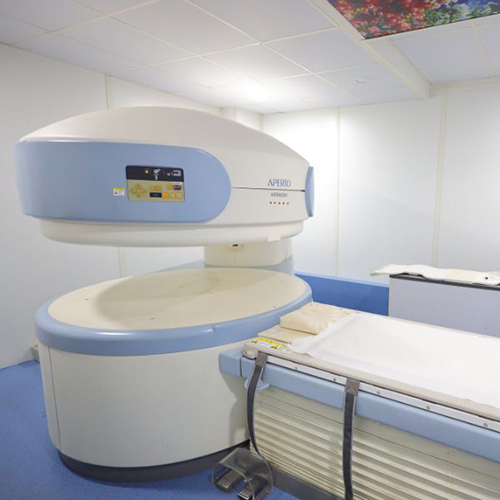
Refurbished Hitachi Aperto Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 14000000 INR
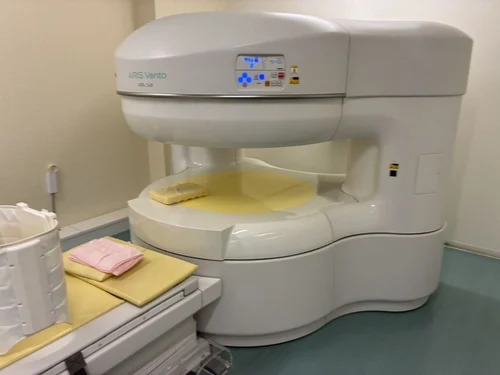
Hitachi Open Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 13500000 INR
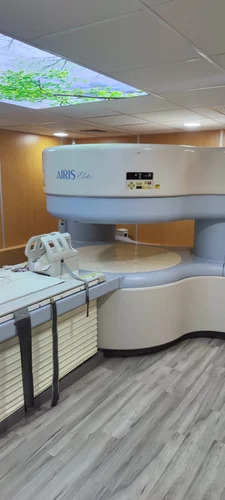
Refurbished Open Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 1000000 INR
Advanced Open Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price: 8500000 INR/Unit
MOQ01 Unit/Units
Display Typemonitor
Warranty3
DisplayColor LCD Monitor
Power Source250
Voltage350 Watt (w)
Divice Medical Systems Pvt Ltd
Secunderabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller1 Years
View More
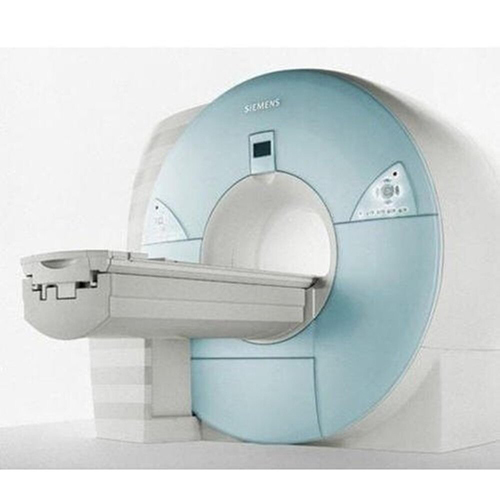
Refurbished Siemens 3T Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price : 6500000 INR
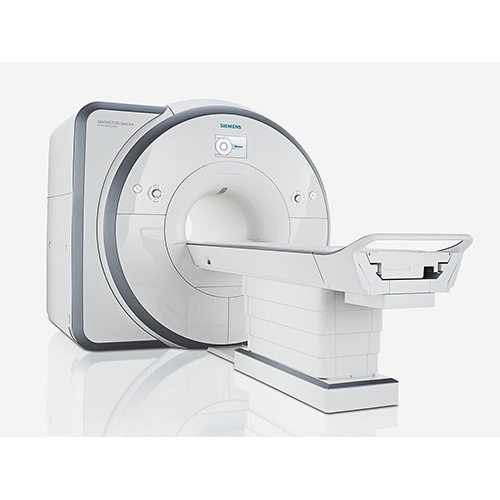
Siemens Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price : 2000000 INR
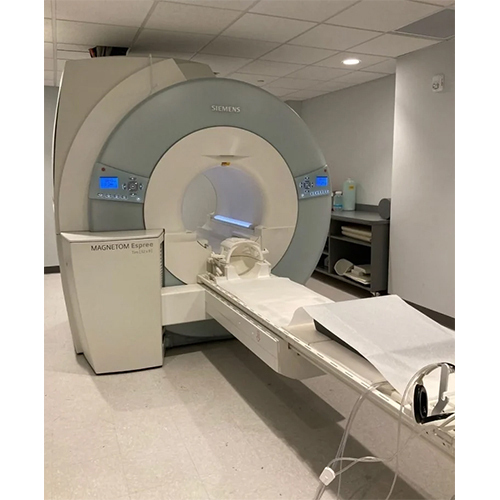
Open Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price : 5500000 INR
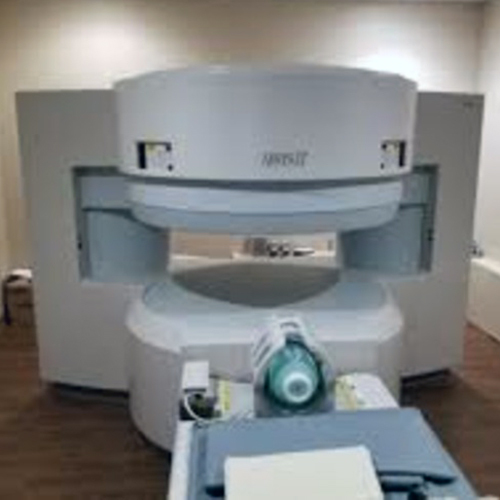
Hitachi Airis Ii 0.3T Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price : 550000 INR
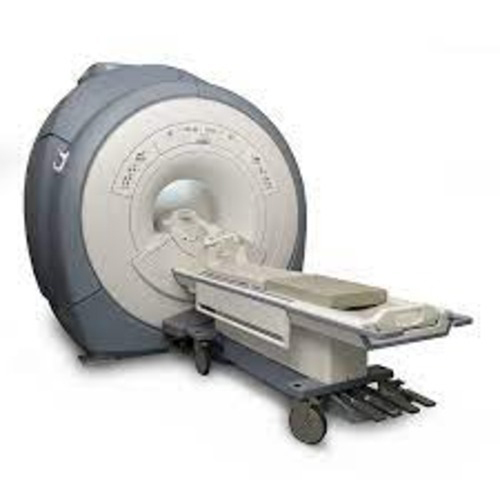
Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5T Mri Machine - Power Source: 250
Price : 7500000 INR
Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5T Mri Machine - Application: Cancer Screening
Price: 27500000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
ApplicationCancer Screening
UseFor medical use
Power220V to 380V Volt (v)
Product TypeGE Signa HDxt 1.5T MRI Machine
Color CodeWhite & Grey
Suitable ForHospitals
Master Medical Systems Llp
New Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller2 Years
View More
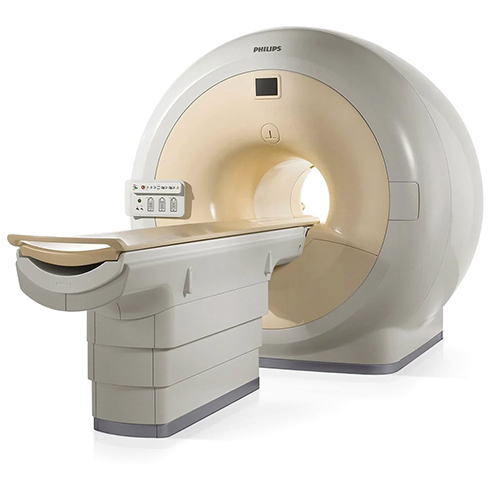
Philips Multiva 1.5 Tesla Mri Machine - Application: Trauma Imaging
Price : 30000000 INR
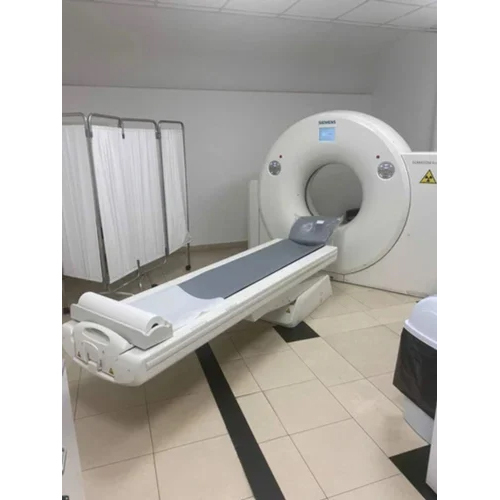
MRI Machine Installation Service
Price : 200000.0 INR
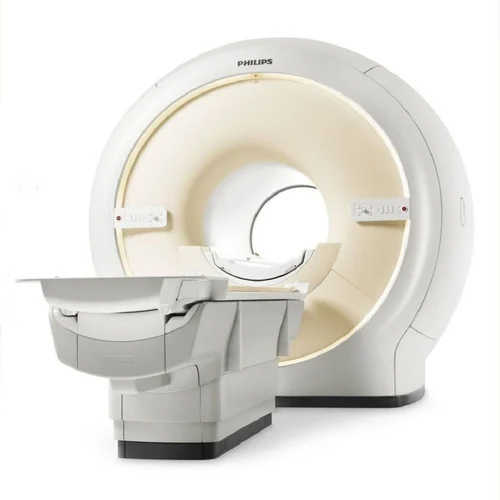
Refurbished Philips Mri Machine - Application: Medical Imaging
Price : 30000000 INR
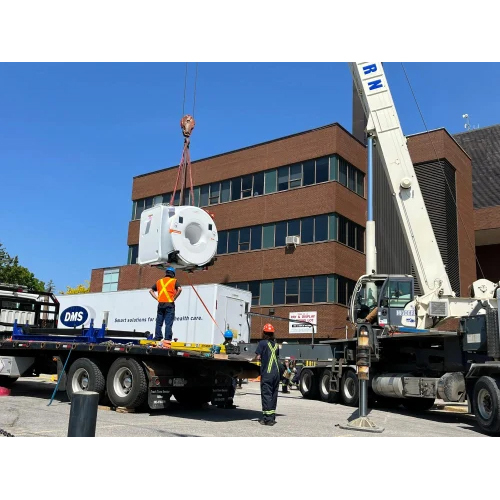

MRI Machine Shifting Service
Price : 2000000 INR
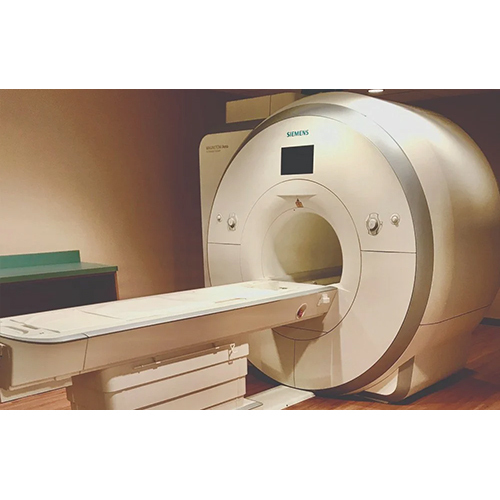
Siemens Refurbished Mri Machine - Application: Trauma Imaging
Price : 30000000 INR
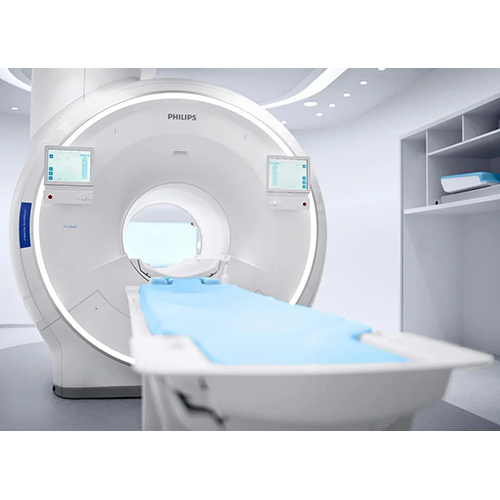
1.5T Philips Mri Machine - Application: Cancer Screening
Price : 30000000 INR
1.5T Siemens Magnetom Avanto Closed Mri Machine - Power: 80 Watt (W)
Price: 30000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeMRI Machine
Power80 Watt (w)
PropertiesHigh Quality
Suitable ForMedical Labs / Hospital
UseCT Scan, MRI Scan
Weight7300 Kilograms (kg)
Professional Healthcare Services
Hyderabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller2 Years
View More
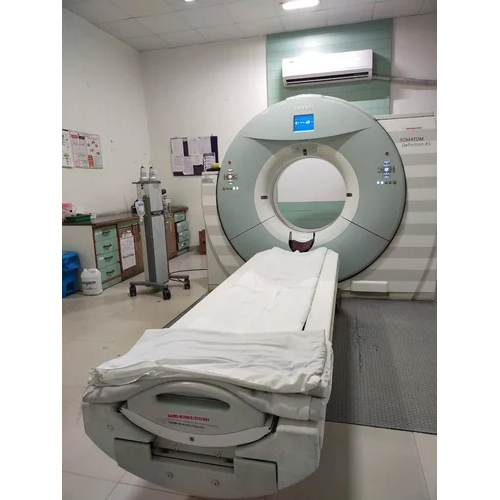
Aera 1.5 Tesla Mri Machine - Power: 55 Watt (W)
Price : 1800.0 INR
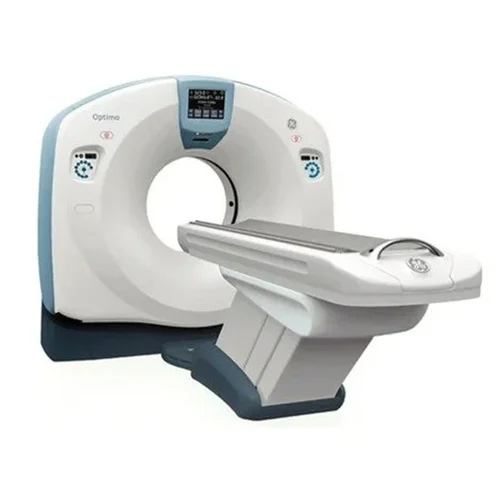
64 Slice GE Optima CT660 CT Scan Machine - 72 Watt Power | High Quality, Suitable for Medical Labs and Hospitals, Advanced CT and MRI Scanning Applications
Price : 6500000 INR
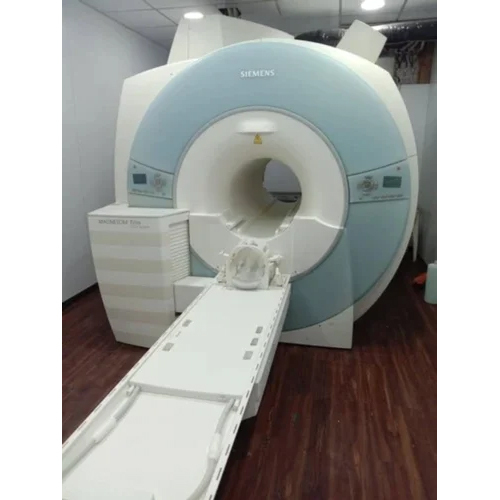
Siemens Magnetom Trio 3T Mri Machine Suitable For: Medical Labs / Hospital
Price : 27500000 INR
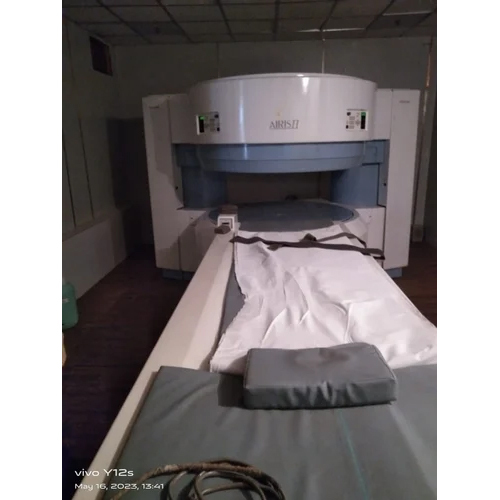

Hitachi Aires 3 Tesla Open Mri Machine - Application: Ct Scan
Price : 26000000 INR
Siemens 1.5 Tesla Mri Machine - Power: 55 Watt (W)
Price : 27500000 INR
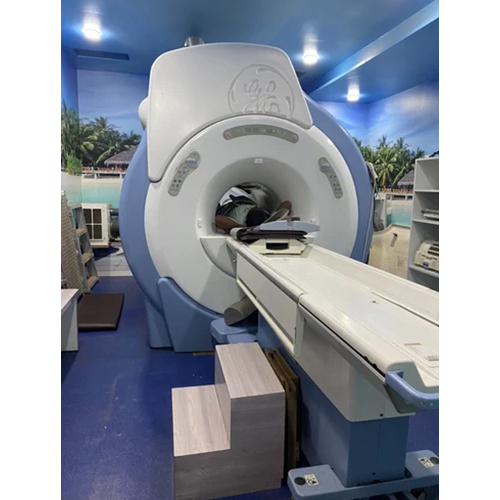

1.5 Tesla Hdxt Ge Mri Machine Suitable For: Medical Labs / Hospital
Price : 26000000 INR
Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price: 3,500,000 INR/Unit
MOQ10 Unit/Units
ApplicationHospital, Laboratory, Diagnostic Centre
Color CodeWhite
MaterialStainless Steel
Product TypeMRI Machine
UseUsed to produce significantly better quality images to give your physician important information in diagnosing your medical condition and planning a course of treatment
Suitable ForChest, Abdomen And Pelvis
View More
Siemens Magnetom Spectra 3T Mri Machine - Application: Commercial
Price : 61000000.00 INR
Closed MRI Scanner - Stainless Steel, High Field Strength (2.5T) | Exceptional Image Quality, Advanced Coil Technology, Patient Comfort Features
Price : 2500000 INR
3T MRI Scanner - Stainless Steel Body, Advanced Imaging Quality | Ideal for Chest, Abdomen, and Pelvis Diagnostics, No Known Side Effects
Price : 2500000 INR
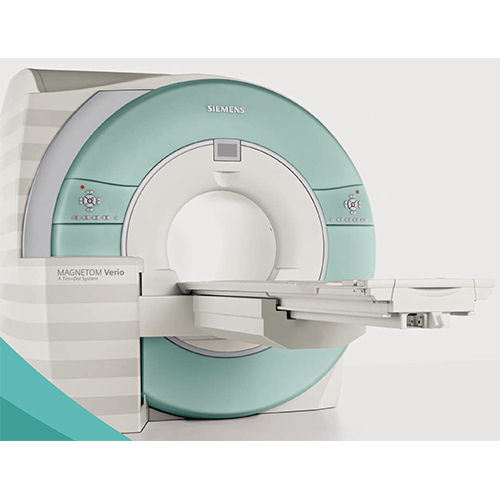
Seimens Verio 3T MRI Machine - Stainless Steel & PVC, High Quality Medical Imaging for Labs and Hospitals
Price : 5100000.00 INR
Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5 T Mri Scanner Machine - Application: Hospital
Price: 30000000 INR/Unit
MOQAny Order Unit/Units,
Product TypeMRI Scanner Machine
ColorStandard White/Grey
MaterialHigh-Grade Components
Color CodeStandard
ApplicationHospital, Lab
PortableNo
Medinnova Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Vadodara
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller5 Years
View More
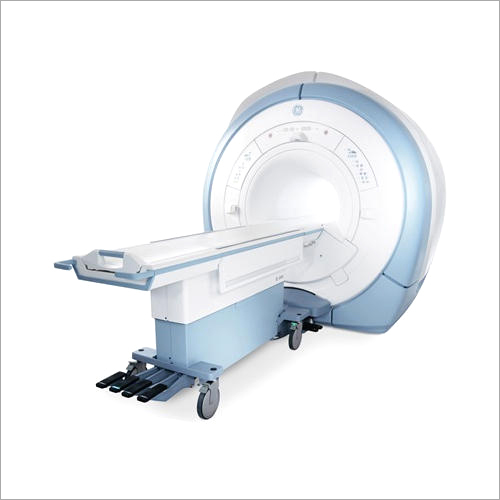
Ge Signa Hdxt 3.0T Mri Scanner Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 62500000 INR
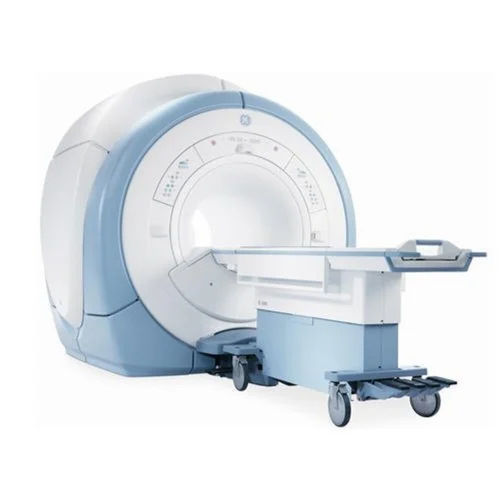
Signa Hdxt 1.5T Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 30000000 INR

Ge Signa Creator Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 32000000 INR
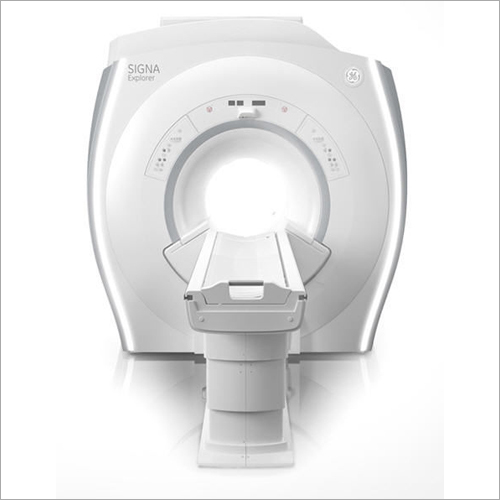
Ge Signa Creator 60Cm 1.5 T Mri Scanner Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 32000000 INR

Discovery Mr750W Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 32500000 INR
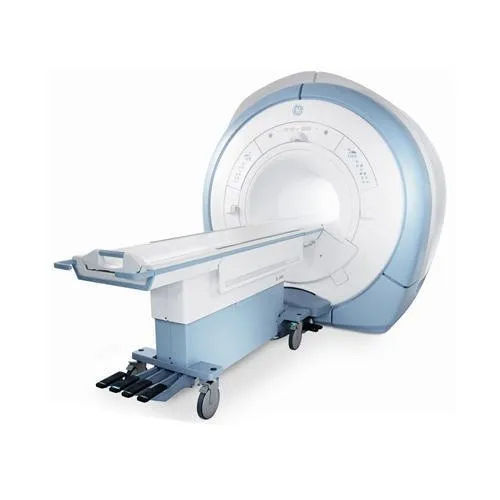
Signa Hdxt 3.0T Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 62500000 INR
Siemens Pre Owend Fully Imported Mri Machine - Application: Commercial
Price: 350000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
PropertiesHigh Quality
MaterialStainless Steel
UseMedical
ApplicationCommercial
Product TypeMRI Machine
Suitable ForHospitals / Lab
Radiance Healthcare Inc
Ranga Reddy district
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller3 Years
Refurbished Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5T Mri Machines Color Code: White
Price: 2,50,00,000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Product TypeRefurbished Ge Signa Hdxt 1.5T MRI Machines
ApplicationMRI
MaterialMetal/Plastic
Suitable ForHuman being
Color CodeWhite
UseHospital
View More
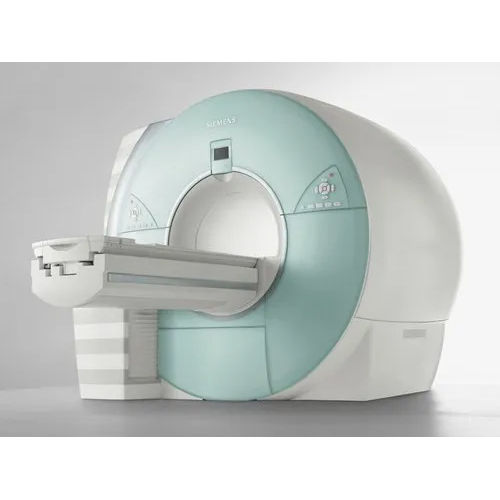
Refurbished Siemens 1.5T Magnetom Avanto Mri Machines Color Code: Customized
Price : 1,65,00,000 INR
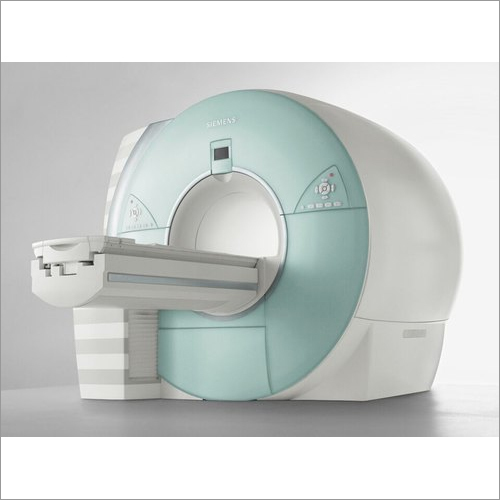
Diagnosis Refurbished Siemens 1.5T Magnetom Avanto Mri Machine
Price : 12500000 INR
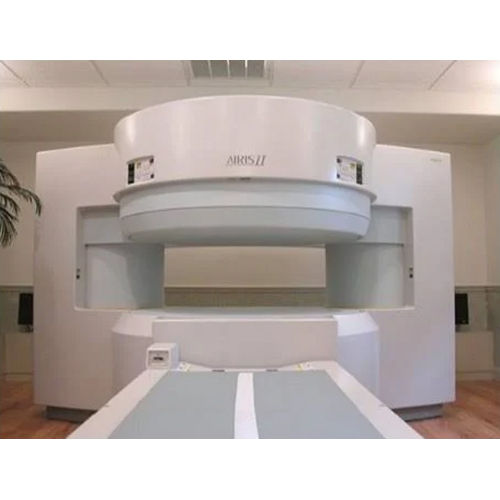

Hitachi Mri Machine Color Code: White
Price : 1,05,00,000 INR
FAQs Related to Mri Machine
This is because gravity cannot assist in moving food and acid through your digestive tract while you are lying flat.
Mri Scan Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price: 27500000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
PortableYes
Temperature Range25 Celsius (oC)
ConditionNew
ColorWhite
MaterialPlastic
UseHospital
Poiya Healthcare (india) Private Limited
Jaipur
 Premium Seller
Premium Seller1 Years
View More
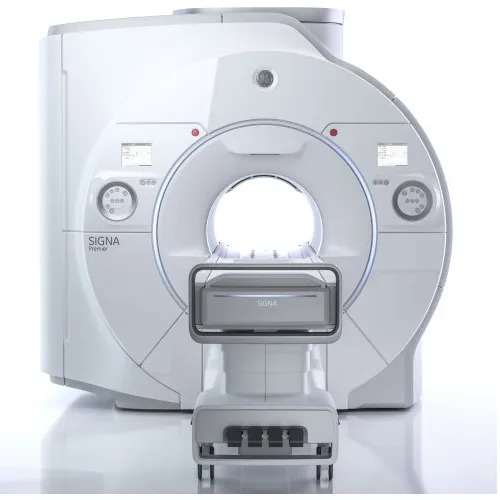
Refurbished Ge 1.5T Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 26000000 INR
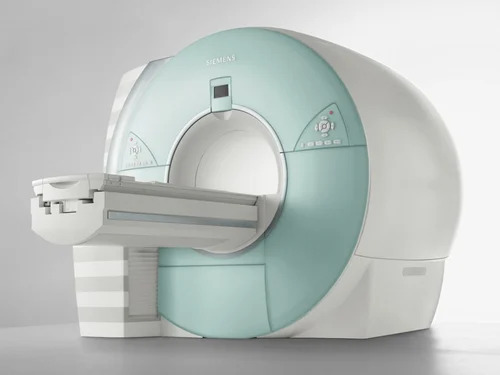
Pre Owned And Refurbished Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 35000000 INR
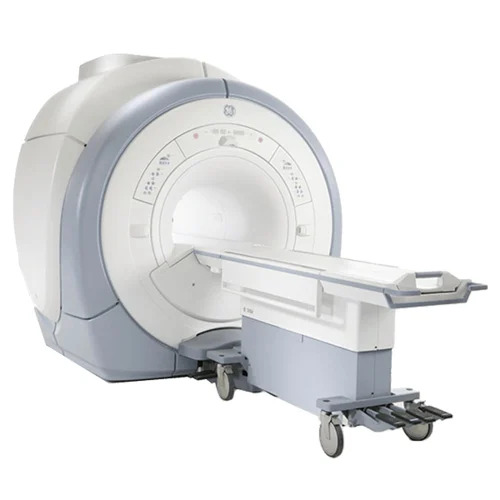
Refurbished Ge 1.5T Mri Machine - Material: Plastic
Price : 26000000 INR
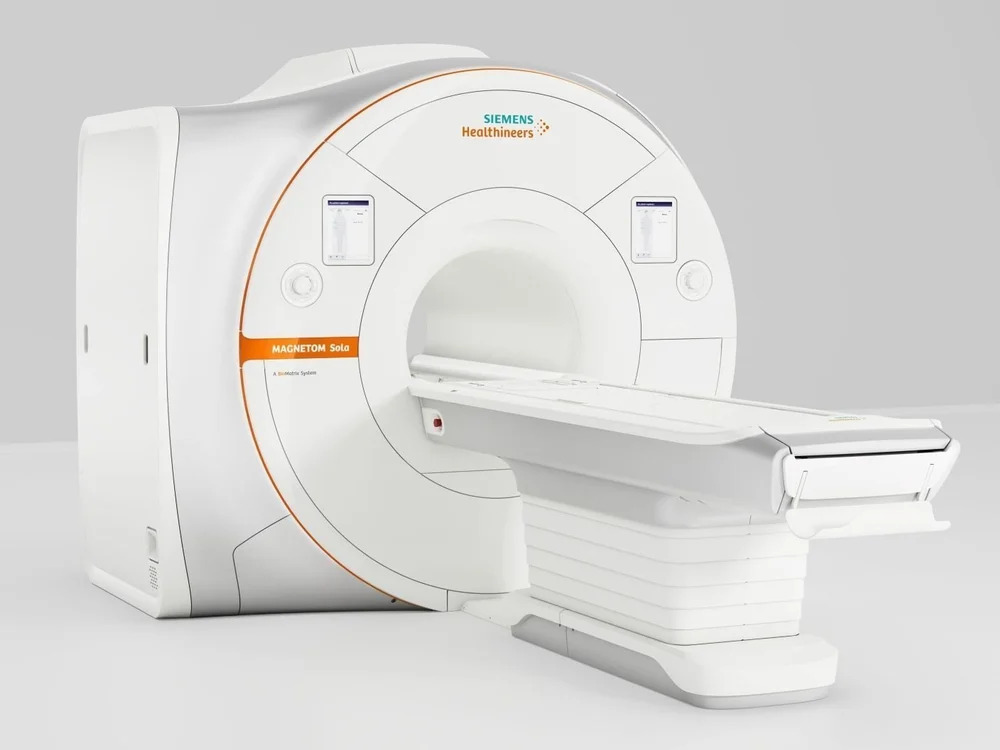
Refurbished Siemens 1.5T Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 25000000 INR
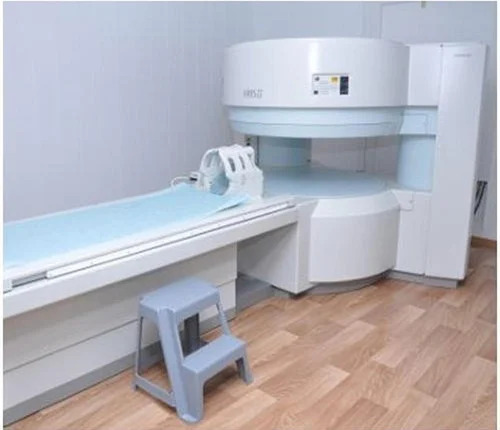
Refurbished Hitachi Airis 2 Mri Machine - Application: Hospital
Price : 15000000 INR
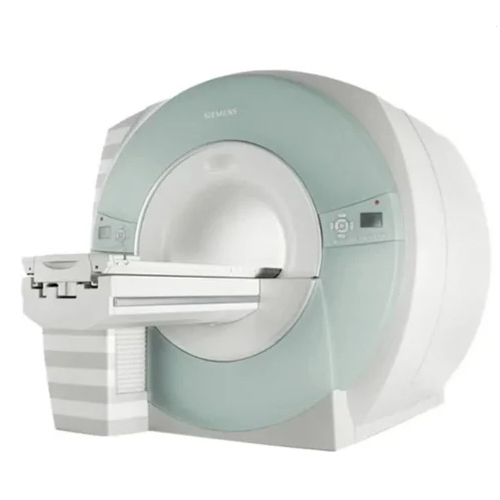
3T Refurbished Siemens Mri Machine - Color: White
Price : 42500000 INR
Linac Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price: 160000000.0 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
ConditionNew
ColorWhite & Green
UseHospital
MaterialPVC
FunctionEasy to use
Automation GradeAutomatic
Shelves Tech Private Limited
New Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller1 Years
Siemens Avanto MRI Scanner System
Price Trend: 27.00 - 29.00 INR/Set
MOQ1 Set/Sets
Power40 kW
Treatment TypeDiagnostic Imaging
Storage CapacityIntegrated patient data storage
Temperature Range15AdegC to 30AdegC
Dimension (L*W*H)500 cm x 250 cm x 200 cm
Height200 cm
Radimage Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Faridabad
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller8 Years
View More
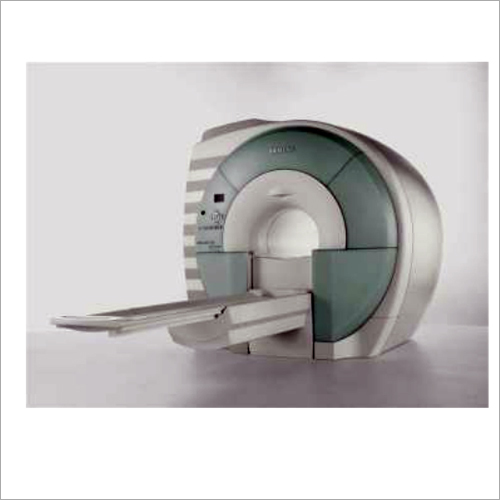
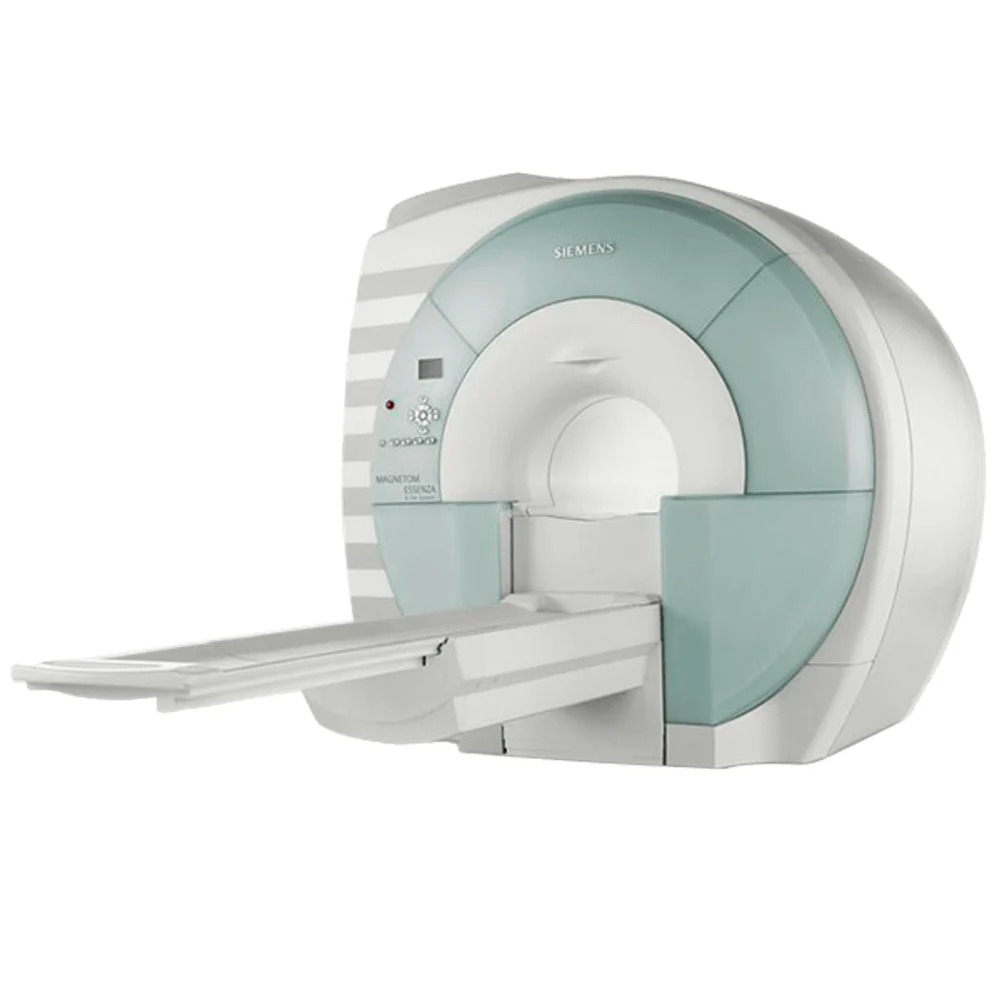
Magnetom Essenza 1.5T MRI Scanner
Price : 19000-17500000 INR
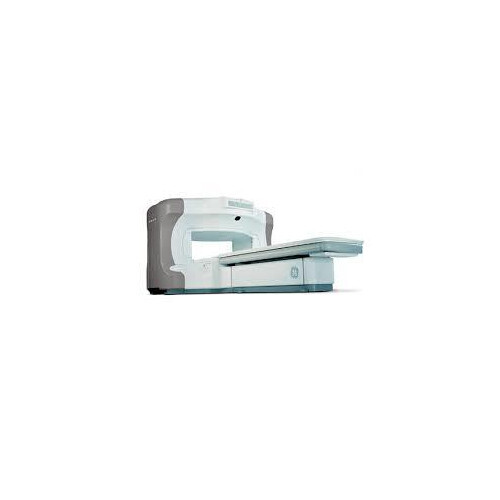

GE Signa Profile 0.2T Open MRI Machine - Stainless Steel and Plastic, Open-Sided Design for Enhanced Patient Comfort and Safety
Price : 17500000 INR
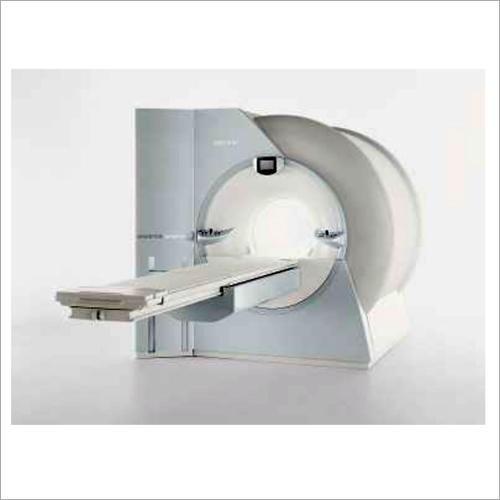
Siemens Magnetom Symphony 1.5t MRI Scanner - 60 cm Bore Diameter, 4,050 kg Magnetic Weight | Reduces Scan Time by 75%, Enhances Efficiency by 20%
Price : 19000-17500000 INR
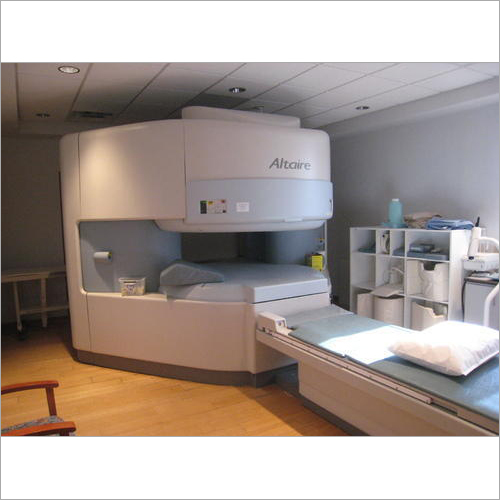
Hitachi MRI Machine - Advanced Imaging Technology | High-Resolution Scans, Ergonomic Design, Patient Comfort
Price Trend : 27.00 - 29.00 INR
Siemens 3.0 T Magnetom Verio MRI Machine - Modern Rectangular Design, Electric Power Source | Ideal for Hospitals
Price: 56000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
ApplicationHospitals
Product TypeMRI Machine
View More
2020 Wide Bore Philips Ingenia Elition X 3T Mri Machine - Attributes: High Quality
Price : 62500000 INR
Philips Achieva 3.0T Mri Machine - Application: Requirement Based
Price : 45000000 INR
3.0 T Mri Ge Machine - Attributes: High Quality
Price : 625000 INR
Refurbished Hitachi Airis Elite Mri Machine - Application: Medical
Price: 12000000 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
UseHospital
ApplicationMedical
Suitable ForHospital
MaterialFRP
Product TypeRefurbished Hitachi Airis Elite MRI Machine
Color CodeWhite
S.B.M. Healthcare (india) Pvt. Ltd.
New Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller Premium Seller
Premium Seller3 Years
View More
Refurbished Siemens 1.5 Tesla Avanto Mri Machine Color Code: White-Light Blue
Price : 27500000 INR

Refurbished Hitachi Airis Mate 0.2T Mri Machine Color Code: White-Light Blue
Price : 8500000 INR
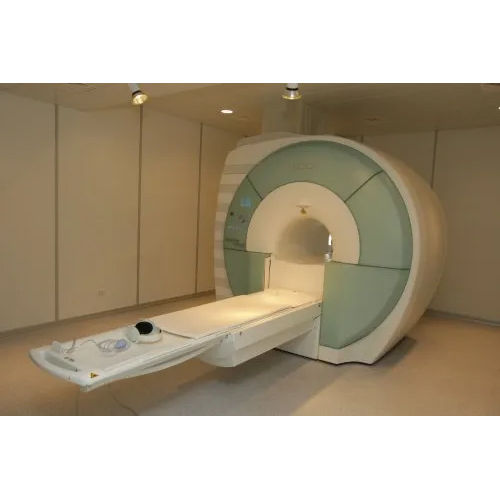
Refurbished Siemens 1.5 T Magnetom Essenza Mri Machine Color Code: White-Light Blue
Price : 29000000 INR

Airis Mate Mri Machine Color Code: White-Grey
Price : 8500000 INR
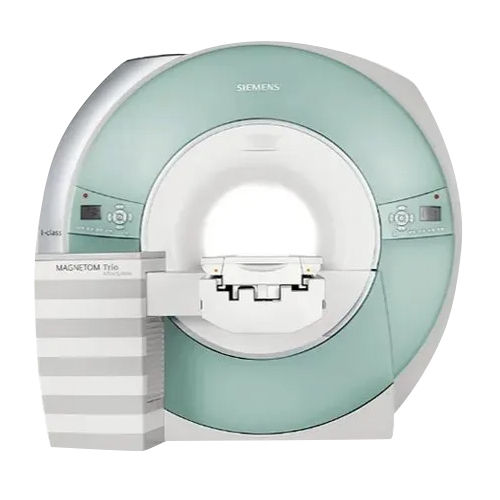
Refurbished Siemens Mri Machine Color Code: White-Light Blue
Price : 28000000 INR

Refurbished Hitachi Airis 2 Mri Machine - Application: Medical
Price : 11000000 INR
MRI Machine - Automatic Operation Mode, New Condition | High-Quality Imaging Equipment in White and Blue, Suitable for Hospital Use
MOQ1 Unit/Units
WarrantyYes
ApplicationHospital
Storage InstructionsDry Place
Suitable For UseMedical purpose
FeatureHigh quality
Operation ModeAutomatic
Refurbished MRI Scanner - High-Quality, Advanced Imaging Technology | Energy-Efficient, Reliable Performance, Comprehensive Diagnostics
Price: 20000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Number
ColorWhite
PortableNo
DisposableNo
Wall MountedNo
Light SourceYes
Real-Time OperationYes
Refurbished Siemens Essenza 1.5T MRI Scan Machine
Price: 34800000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeRefurbished Siemens Essenza 1.5T MRI Scan Machine
FeatureLow Maintenance
Automation GradeAutomatic
Equipment TypeMRI
Storage InstructionsRoom Temperature
MaterialPlastic
View More
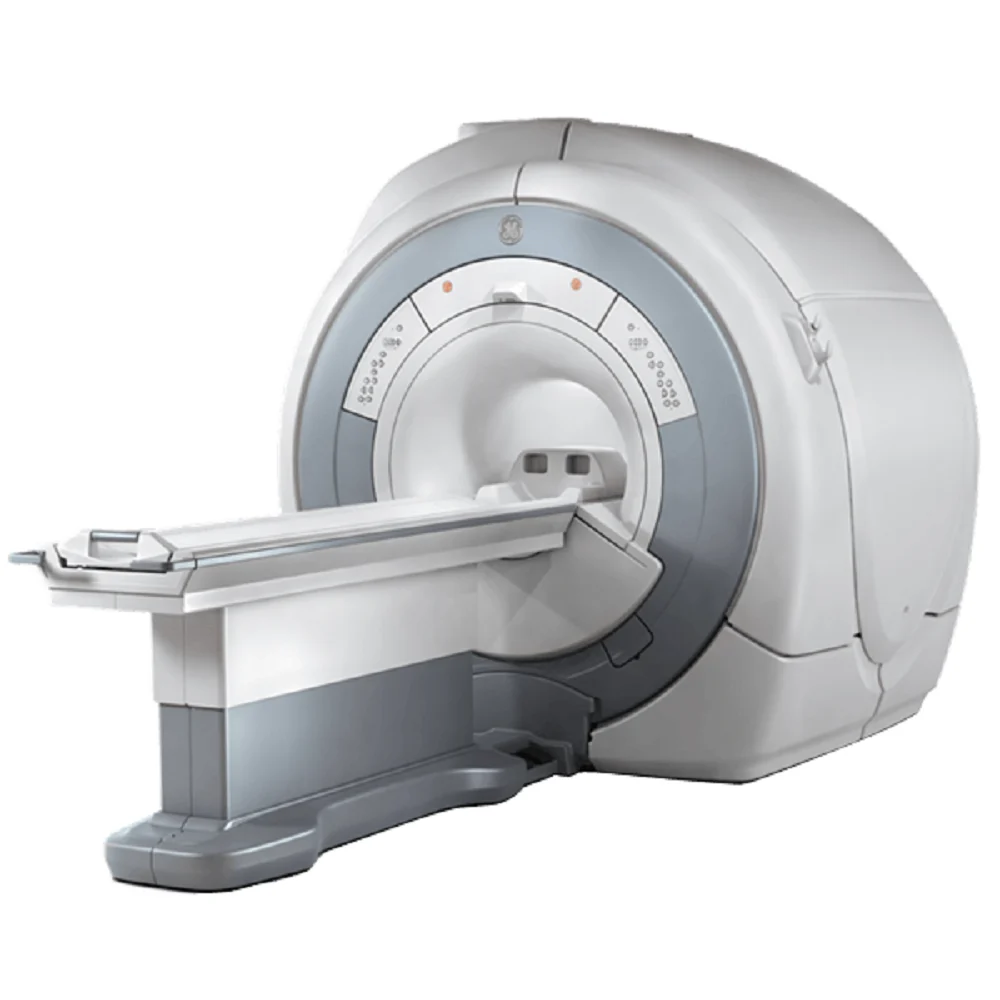
Refurbished GE HDe MRI Machine
Price : 32500000 INR
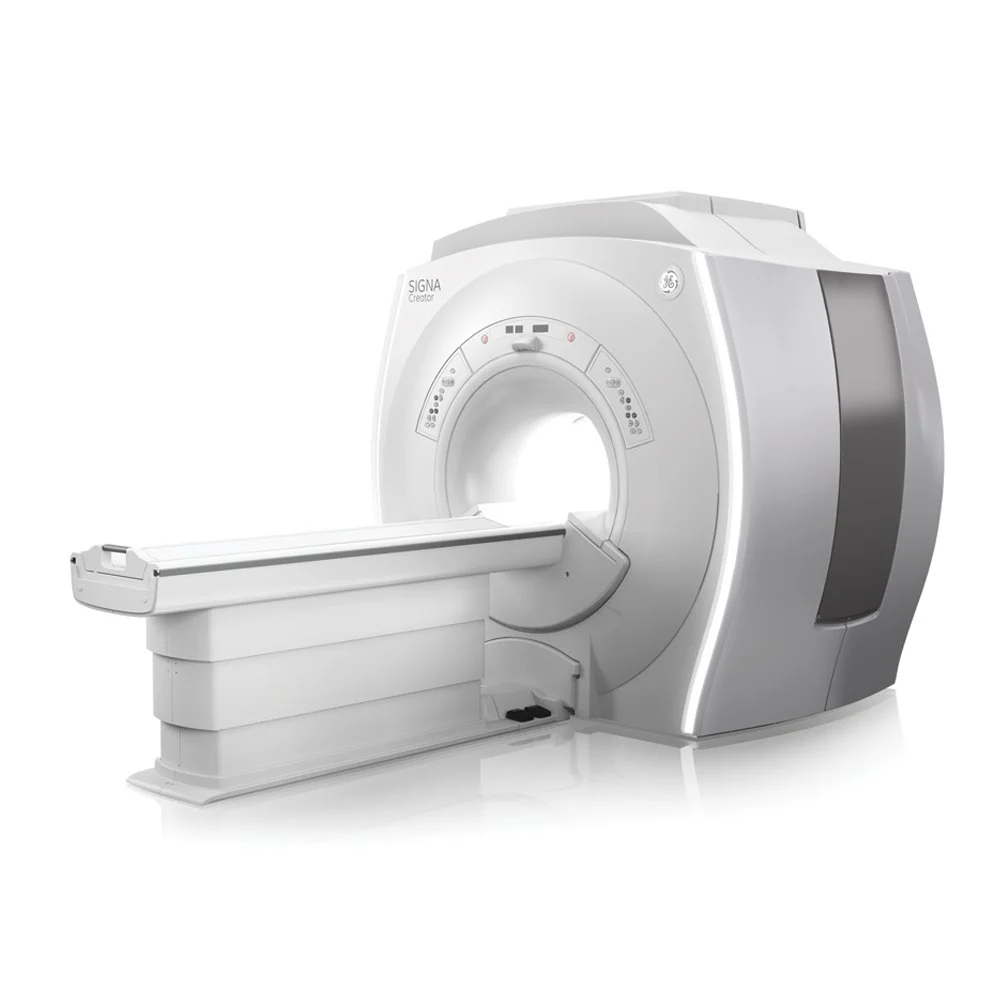
Refurbished GE Signa Creator MRI Scan Machine
Price : 33700000 INR
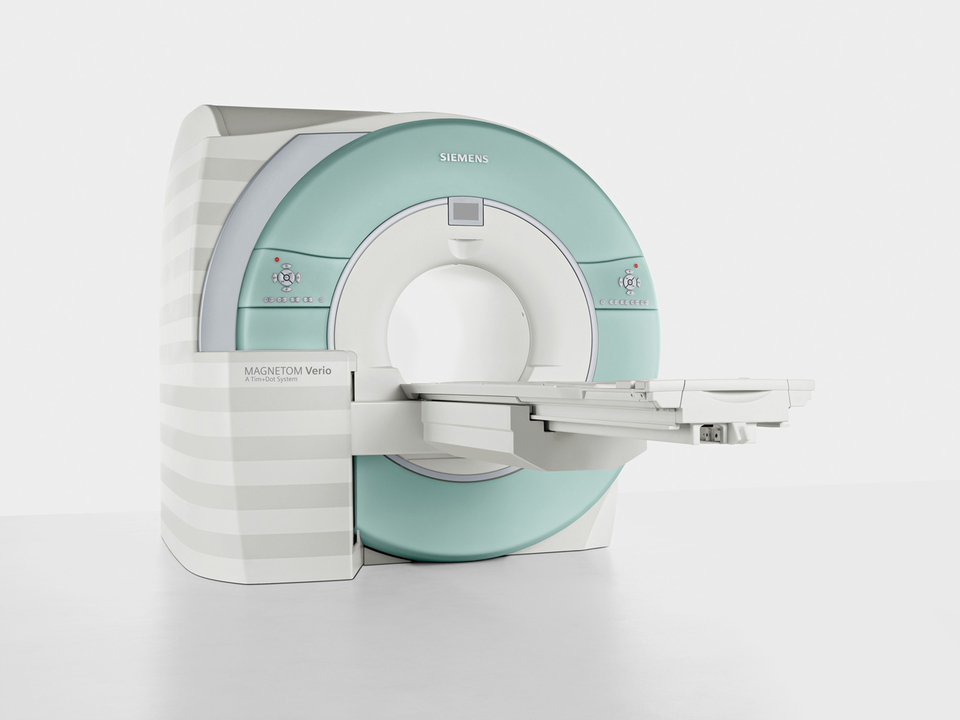
Used Siemens Magnetom Essenza 1.5t Mri Machine
Price : 3000000 INR
MRI Scanner Machine - High-Strength Non-Magnetic Alloys, Plastic, and Composite Materials | Reliable Medical Imaging for Neurology, Orthopedics, Cardiology, and Oncology
Price: 2750000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeMRI Scanner
UseDetects brain tumors, strokes, and multiple sclerosis
ApplicationMedical imaging for neurology, orthopedics, cardiology, oncology, and general diagnostics
MaterialHigh-strength non-magnetic alloys, plastic, and composite materials
Color CodeWhite, Light Gray, or Blue
Power30 kW to 100 kW Volt (v)
Ge Refurbished 3T Mri Machine - Material: Stainless Steel
Price: 2500000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
MaterialStainless Steel
Warranty1 Year
UseHospital
ConditionNew
DisplayDigital
Power SourceElectric
View More
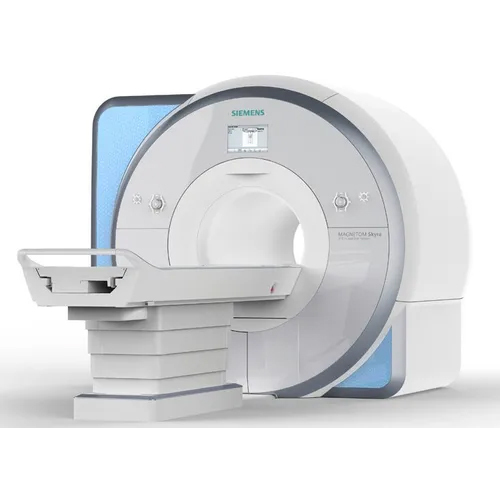
Siemens Refurbished 3T Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 20000000 INR
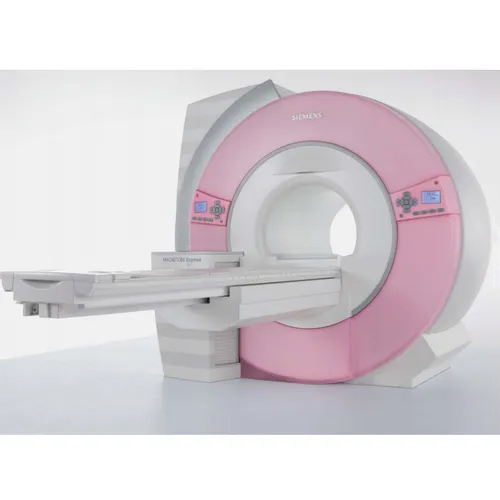
Refurbished Siemens 0.3T Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 9000000 INR
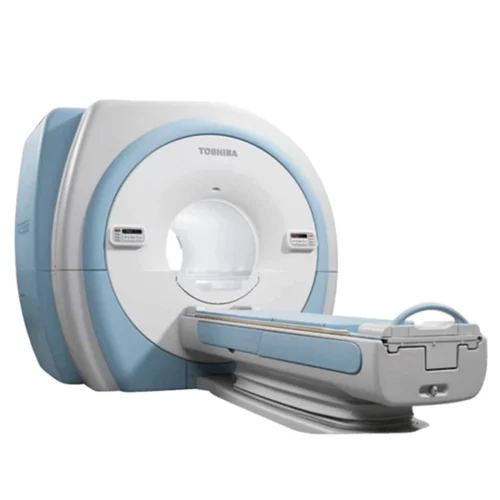
Refurbished 3T Toshiba Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 32000000 INR

Refurbished Ge 0.3T Mri Machine - Material: Stainless Steel
Price : 1850000 INR
Siemens Refurbished 1.5T Mri Machine - Material: Stainless Steel
Price : 17800000 INR
Ge Refurbished 1.5T Mri Machine - Automation Grade: Automatic
Price : 18000000 INR
Medical Mri Machine Application: Hospital
Price: 7500000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
UseScanning
PropertiesHigh Quality
ApplicationHospital
Product TypeMedical MRI Machine
Suitable ForHuman being
Hospital Mri Machine - Color Code: White
Price: 20000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Dimension (L*W*H)Different Size Millimeter (mm)
Suitable ForHospital
Color CodeWhite
MaterialStainless Steel
ApplicationHospital
WeightAs per available Kilograms (kg)
The South India Surgical Co (bangalores)
Bengaluru
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller1 Years
Aparto MRI Machine - 4.95 Tesla Magnetic Field Strength | Advanced Imaging Technology, Patient-Friendly Design, Energy-Efficient Diagnostics, Intuitive User Interface
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Suitable ForHospital, Diagnostic Centre
UseUsed for whole body scanning
ApplicationDiagnostic, Hospital
Product TypeAparto MRI Machine 4.95CR
Color CodeWhite
View More
Refurbished 1.5T Siemens Mri Machine - Accuracy: 99 %
Price : 28500000 INR
Refurbished Mri Scanner Machine Application: Hospital
Price: 16000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeRefurbished MRI Machine
ApplicationHospital
Color CodeGray
View More
Refurbished Ge Mri Machine
Price : 2750000 INR
Refurbished Mri Machine Application: Hospital
Price : 8000000 INR
Refurbished Siemens 3t Mri Machine
Price: 20000000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Automation GradeAutomatic
ConditionNew
MaterialMild Steel
DisplayDigital
Voltage220/380 Volt (v)
Power SourceElectric
Fabius Mri
Product TypeFabius MRI
MaterialPlastic
Suitable ForPatients
ApplicationHospital
Color CodeGray & Blue
Usefor Patient Monitoring
Popular Mri Machine
How MRI Machines are Essential for Medical Diagnostics
MRI machines are useful machinery for medical diagnostics. It helps to take a perfect image of the internal organs and any active parts of the body. Let’s see the benefits of the MRI machines in this section.
- Non-Invasive: MRI scan doesn't use ionizing radiation like X-rays.
- High-resolution images: It helps to produce high-resolution images of the inside of the body.
- Soft tissue imaging: It helps to capture the image of soft tissues like muscles, tissues, and tendons.
- Brain imaging: It provides help in imaging the brain and spinal cord.
- Functional MRI: MRI helps for the scanning to identify the active parts of the brain while doing the task.
- Wide range of applications: MRI scans are used in different kinds of situations like tumors, injuries, and diseases of the brain, heart, and digestive organs.
Why Are MRI Machines Essential?
MRI machines are useful in the medical industry for accessing detailed, non-invasion images of soft tissues within the body. It helps doctors to diagnose a wide range of conditions to affect the muscles, ligaments, tendons, organs, and the nervous system. With its usage, it provides an accurate image without the use of harmful X-rays or CT scans. It has many benefits for the medical industry like visualization of soft tissues, strong magnetic field with no exposure, a wide range of applications, functional MRI, and helps to plan the surgery and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Advanced MRI Machine Technology
MRI machine technology is equipped with many advanced technologies. It helps to provide a better technically advanced solution to provide improved quality of image and speed.
High-field MRI systems
- 7T and 10T MRI: It produces sharper images than traditional 1.5T or 3T MRI machines.
- Iseult MRI: It has a magnetic field of 11.7 Tesla, for taking detailed images of the brain.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Deep Resolve: The AI-powered workflow uses deep neural networks to improve image quality and speed up imaging.
- Motion artifact reduction: AI algorithms can reduce motion artifacts in 3D images.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
The use of functional magnetic resonance imaging allows medical professionals to see brain activity in real-time.
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
It is used to study brain tumors, strokes, and other brain diseases.
iMRI
It helps to provide surgeons with detailed images of the anatomy during procedures.
Benefits of Clear MRI Imaging
The medical industry requires lots of accuracy to deal with the problems of patients. So the requirement of accurate machines will add benefits to the doctors in the diagnosis. It has the benefits like:
-
Soft Tissue Imaging
A clear MRI image is better at distinguishing between soft tissues, like muscle, fat, and water, than CT scans.
-
Brain Imaging
Clear MRI images can differentiate between white and gray matter in the brain.
-
Heart Imaging
Clear MRI can detect tumors and determine their size and spread.
-
Injury Assessment
Clear MRI can image knee and shoulder injuries.
-
Functional Imaging
Functional MRI (fMRI) can pinpoint the exact location of brain activity during specific tasks.
-
Early Diagnosis
Clear MRI images can help identify disease early.
-
Treatment Evaluatio
Clear MRI imaging can check how well a treatment is working.
Client Testimonials & Reviews

ManishVyas
WESTERN SURGICAL
We are grow our business with tradeindia. This is a very good platform for Globally your business Expansion also tradeindia Give Us good Space for built up our BrandA

NazimMunshi
MN LIFE CARE PRODUCTS PVT. LTD.
Daily visit in Tradeindia is like visiting any social site to me. I am associated with Tradeindia.com from past 4 years and in this 4 years this co gave me no reason to invest on other B2B portal. In one word it is the actual "SATISFACTION" or "SUCCESS" which i met through them (tradeindia). I am sure people who have invested and will invest here for their business promotions and growth are the successful persons and their decision to invest here is best business idea/venture ever.

AndyChou
ZS ENTERPRISE CO., LTD.
My company ZS ENTERPRISE CO LTD has joined tradeindia for 6 years back. We are happy with the service, promotion and response. It has help us to develop good business in international market, we get good inquiries using the platform and the support we get from the account manager is appreciated. Thanks for that, and we expect more good business in the upcoming years.

MeenakshiAron
YOUNG BROTHERS
Overall experience with tradeindia is satisfactory, Tradeindia app is a good one from where I get inquiries from various customers and is a easy-business handling app.

SunilDutt
CREATIVE HEALTH TECH PVT. LTD.
We are having good working experience with tradeindia, they are expertise in B2B segment in India and overseas market. They promoted our company very well and received more business inquiry. We wish tradeindia to give more business also in coming years. We wish long term business association with tradeindia.com.

VishnuChaudhary
MEDIRAY HEALTHCARE
We associated with tradeindia. This has helped us to exponentially to expand our presence not only Domestically with in India but also in different International markets. We look forward to a continual relationship with tradeindia.com and recommended to others, as one of the most organized B2B platform for branding of our products and services.

MrAvichal
INDIA MEDICO INSTRUMENTS
Now a days, I am working from home and getting good support from tradeindia, while adding new products. Thanks.

KirtiVerma
KANNU IMPEX (INDIA) PVT. LTD.
We associated with tradeindia.com and we are able to generate a customer base service of our company. There service is excellent and packages are very fruitful and good for us.

DEEPAKJOSHI
DEVPARV SURGICO
Our company has been a member of tradeindia from 2004. We are happy with the service provided by tradeindia to promote our products to our clients all over the world. It has helped us to increase our visibility.The team from tradeindia are also constantly interacting with us to help and improve our online marketing.

MandeepSethi
Modsurg Equipments
We are member of Tradeindia.com from last 10years and we are very much satisfied with the services of Tradeindia. It's very useful to improve my promotion as well as business. We are very thankful to team Tradeindia.
Mri Machine Price List
Product Name | Expected Price |
|---|---|
| 7m MRI Coil | 300000 |
| Used Siemens Magnetom Essenza 1.5t Mri Machine | 3000000 |
| Refurbished Siemens Essenza 1.5T MRI Scan Machine | 34800000 |
| Refurbished Siemens 3t Mri Machine | 20000000 |
| Wdm Xpert 0.5t Open Mri | 6700000 |
| Refurbished 1.5T Siemens MRI Machine | 28500000 |
| GE Signa HDXT 1.5T MRI Machine | 7500000 |
| Refurbished Siemens 3T MRI Machine | 6500000 |
| Siemens MRI Machine | 2000000 |
| Advanced Open MRI Machine | 8500000 |
This Data was Last Updated on 2025-12-22
Mri Machine Manufacturers | Suppliers in India
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Radimage Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Faridabad, India | 8 Years |
Premier Medical Corporation Chennai, India | 6 Years |
Hi Touch Instruments Pune, India | 6 Years |
Benaka Health Care Bengaluru, India | 6 Years |
Medinnova Systems Pvt. Ltd. Vadodara, India | 5 Years |
Sonomatrix Medicare Lucknow, India | 4 Years |
Radiance Healthcare Inc Ranga Reddy district, India | 3 Years |
S.b.m. Healthcare (india) Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi, India | 3 Years |
Sbm Health Care Coimbatore, India | 3 Years |
Radscan Systems Private Limited Delhi, India | 2 Years |
Upcoming Tradeshows
CWIEME Shanghai 2026
Wed, 24 Jun, 2026 - Fri, 26 Jun, 2026
INDOMACH Jamshedpur 2026
Thu, 05 Feb, 2026 - Sun, 08 Feb, 2026
Asia Photonics Expo (APE 2026)
Wed, 04 Feb, 2026 - Fri, 06 Feb, 2026
IFF - India Fashion Forum 2026
Wed, 28 Jan, 2026 - Thu, 29 Jan, 2026
Plastic Packaging Printing Expo (P3) 2026
Fri, 10 Apr, 2026 - Mon, 13 Apr, 2026
STEEL CONSTRUCTION EXPO 2026
Thu, 26 Feb, 2026 - Sat, 28 Feb, 2026
Panacea - Natural Products Expo India 2026
Fri, 06 Mar, 2026 - Sun, 08 Mar, 2026
India Boat & Marine Show 2026
Thu, 29 Jan, 2026 - Sat, 31 Jan, 2026
Spectra Expo 2026
Wed, 06 May, 2026 - Fri, 08 May, 2026
Odisha Mining & Infrastructure International Expo 2026
Thu, 08 Jan, 2026 - Sun, 11 Jan, 2026
Popular Categories