Process Control Equipment & Instruments
(2944 products)Product Showcase
Air Flow Studies Apparatus - Application: Laboratory
By:
Didac International
SIEMENS SCADA 6AV2100-0AA02-3AH5
By:
Naksh Technology
Variable Speed Drives - Application: For Crane And Elevetor
By:
Mifa Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Weatherproof Loop Power Indicator (Lpi-400 Wp) Accuracy: Linear : +/-0.1 Percent Of Span ; Square Root : +/-0.2 Percent Of Span %
By:
Ambetronics Engineers Pvt. Ltd.
Naksh Technology Solution Llp
Ahmedabad
Variable Speed Drives - Application: For Crane And Elevetor
Price Trend: 13900.00 - 32200.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Product TypeVFD
ApplicationFor Crane and Elevetor
Protection LevelIP55
Frequency (MHz)50 Hertz (HZ)
Rated Voltage415 Volt (V)
Energy Consumption.75 Kilowatt-hour ( KWH)
Weatherproof Loop Power Indicator (Lpi-400 Wp) Accuracy: Linear : +/-0.1 Percent Of Span ; Square Root : +/-0.2 Percent Of Span %
Price Trend: 1000.00 - 10000.00 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
AccuracyLinear : +/-0.1 Percent of span ; Square root : +/-0.2 Percent of span %
Size120(H) x 100(W) x 60(D) in mm
Ambetronics Engineers Pvt. Ltd.
Mumbai
Orifice Plates - High-Quality Stainless Steel, Differential Pressure Measurement | Durable and Reliable Performance
Product DescriptionKnowing us as a reputed firm, we are engaged in manufacturing, supplying as well as exporting a wide range of Orifice Plates from Vadodara, Gujarat, India. We don't reduce on quality subsequently we obtain crude material from solid source. It is used differential pressure measurement. One can avail
Digital Process Controller - Color: Black
Price: 3700 INR/Piece
MOQ10 , Piece/Pieces
ColorBlack
Power100-240 Volt (v)
Voltage24VDC Volt (v)
UsageIndustrial
SizeStandard
Procon Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad
Flanged Thermowell - Color: Sliver
ColorSliver
UsageIndustrial
Operate MethodAutomatic
PressureUp to 5000 PSI
AccuracyA+-0.5%
ConnectionFlange
Precihole Machine Tools Pvt. Ltd.
Bhiwandi
Belt Way Weighing Controller Accuracy: Wide Range Of Accuracy %
Price Trend: 30000.00 - 200000.00 INR/Set
MOQ1 Ton/Tons
ConnectionRs 232
Voltage230 Volt (v)
Product TypeAutomatic
Power230 Volt (v)
FunctionAutomatic
Servo Controller
Price: 26000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
Power24V DC Volt (v)
CapacityIndustrial heavy duty Ton
Connection24V DC
ColorGray
UsageBag making Machine Cut to Length application
Weight500 Grams (g)
Methyl Orange - Application: Industrial
MOQ50 Kilograms/Kilograms
UsageLaboratory
Product TypeMethyl Orange
ColorMulticolour
ApplicationIndustrial
FunctionMethyl Orange works as pH indicator and finds suitability in titrations as it provides for changing color at pH of mid-strength. We can offer it in tamper proof finish in both standard as well as customized packaging support that meets the industrial standards.
SizeStandard
Level Sensing Controller For Cement Industries - Color: Orange And Silver
Price: 14250.0 INR/Piece
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
MaterialStainless Steel
Current15 to 80 VDC and 15 to 260 VAC Volt (v)
ApplicationIndustrial
Operate MethodVibrating
Accuracy1 %
Product TypeLevel Sensing Controller For Cement Industries
Thyristor And Diode Converters - Application: Industrial
Price Trend: 50000.00 - 500000.00 INR/Pack
MOQ1 Pack/Packs
ColorMulticolor
MaterialMetal
UsageIndustrial
ApplicationIndustrial
FunctionLab
SizeStandard
Didac International
New Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller11 Years
Dew Point Analyzer - Accuracy: +/-1 %
Price: 118600.00 INR/Pack
MOQ1 Pack/Packs
Weight0.5 Kilograms (kg)
MaterialAluminum
Accuracy+/-1 %
Connection1/4 "
Product TypeFixed
UsageIndustrial
Applied Techno Engineers Private Limited
Vasai
Pressure Transmitter - Stainless Steel, 110-220 Voltage | Industrial Application, Precise Pressure Measurement
MOQ1 Piece/Pieces
Voltage110-220 Volt (v)
ApplicationIndustrial
MaterialSS
Product TypePressure Transmitter
Honeywell Pressuretrol L91b
Product DescriptionWe manufacture, distribute, trade and supply Honeywell Pressuretrol in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. Our Honeywell Pressuretrol L91B for Boiler Pressure Control applications. Our Honeywell Pressuretrol L91B is available in various sizes and specifications. These Honeywell Pressuretrol L91B are availabl
Swimming Pool Digital Controller - Color: White
Price: 250000 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
MaterialPVC
Operate MethodAutomatic
UsageSwimming Pool
Voltage220 Volt (v)
ColorWhite
ShapeRectangular
Fastening Counter Controller
Product DescriptionUryu Fastening Counter Controller Model, UTM-1100, count down the number of bolts or nuts after fastened by the TM-type of Oil-Pulse Tool or impact wrench modified to sense the back pressure from the tool.This remarkable function automatically makes sure of perfect fastening of all the required num
Central Monitoring Management System
Price Trend: 280000.00 - 450000.00 INR/Unit
MOQ1 , Unit/Units
Supply Ability10 Per Month
Delivery Time2-12 Week
R. B Electronic & Engineering Pvt. Ltd.
Chanod
Ph Indicator - Color: Blue
Price: 12400 INR/Unit
MOQ1 Unit/Units
UsageIndustrial
Operate MethodManual
Product TypePH Indicator
ColorBlue
MaterialMetal
Pm2.5 Air Quality Sensor - Application: Industrial
Price: 11000 INR/Unit
MOQ10 Unit/Units
Voltage12 Volt (v)
Product TypePM2.5 Air Quality Sensor
MaterialABS
ApplicationIndustrial
ColorBlack
SizeStandard
Process Automation - High-Quality Compliance Manufacturing | Streamlined Efficiency, Competitive Pricing
Product DescriptionWe are presenting to our esteemed customers a high quality Process Automation. These are manufactured under highly strict measures in order to maintain its compliance with the well-defined quality standards. Moreover, clients can obtain these from us at most competitive price
Yudian Make Touch Screen Data Logger Accuracy: 0.2% %
Price: 15000 INR/Number
MOQ1-100 Number
Dimension (L*W*H)135X96mm (WXH) Millimeter (mm)
Usagetemperature, pressure, humidity, voltage and current data loggers. Multi-input data loggers can measure signals from two or more of these input sources; certain advanced multi-channel models may even be able to sense and record all of the above
Accuracy0.2% %
ClassificationCE
Weight1 Kilograms (kg)
ApplicationData Logging and Monitoring
Micon Automation Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad
Electronic Control Unit Model MLC03
Product DescriptionOverall Dimension: 96 x 96 x 65mm\015\012Mounting: Flush Panel\015\012Panel Cutout: 94x94\015\012Mains Power Supply: 230 VAC / 24 VDC\015\012Input Signal: Float Switch Contacts\015\012Output: 3 Potential free Changeover Relays with latching contacts\015\012Contact rating: 5 A at 230 VAC Res.\015\012
Temperature Transmitter
Price Trend: 5500 - 32000 INR/Number
MOQ1 Number
Supply Ability10 Per Day
Delivery Time24 Hours
Main Export Market(s)Middle East, Western Europe, Africa, Central America, Eastern Europe, South America, Asia, North America, Australia
Ishwar Climate Solutions Private Limited
Mumbai
Double Stage Double Gauge Co2 Regulators
Product DescriptionThese Double Stage Double Gauge CO2 Regulators are made from very high quality raw material which ensures hassle free work performance at its user end. These Double Stage Double Gauge Regulators are technologically advanced and confirm to industrial quality norms of international standard. These are
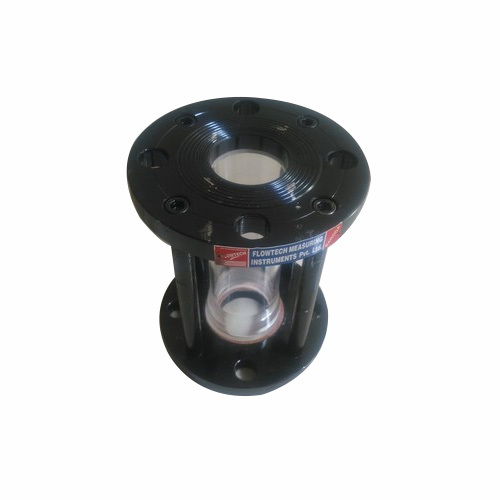
Sight Glass - MS, CS (A-105), SS304, SS316 | Sizes 15 to 300 mm, Maximum Pressure 25 kgf/cm2, 360-Degree Visibility for Liquid Flow Monitoring
Price Trend: 5000.00 - 15000.00 INR/Box
MOQ50 Box/Boxes
UsageChemical, Water
MaterialM.S, C.S. (AaEUR"105), S.S.304, S.S.316, or MS with Rubber or PP or PVDF or Teflon lined or any other alloy.
ClassificationLevel Indicator
Product TypeSight Glass
ApplicationChemical Industry
Pressure25 kgf/cm2
Flowtech Measuring Instruments Pvt. Ltd.
Vadodara
Overload Safety Switch
Product DescriptionWe offer our client an excellent quality range of Overload Safety Switch, which are manufactured from high grade quality raw materials. These can be customized as per our precious customers specifications. These are widely known for its durability and quality. Our can be availed at industrial leadin
Silverline Metal Engineering Pvt. Ltd.
Mumbai
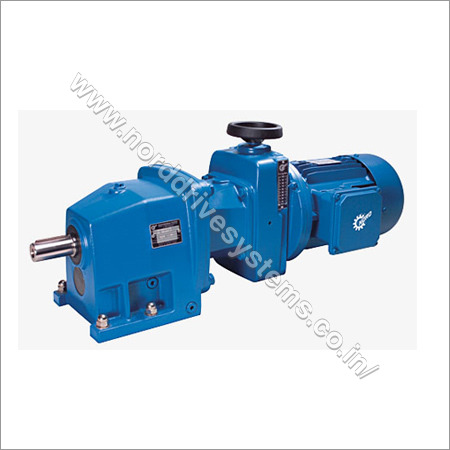
Nord Drivesystems Pvt. Ltd.
Pune
 Premium Seller
Premium Seller15 Years
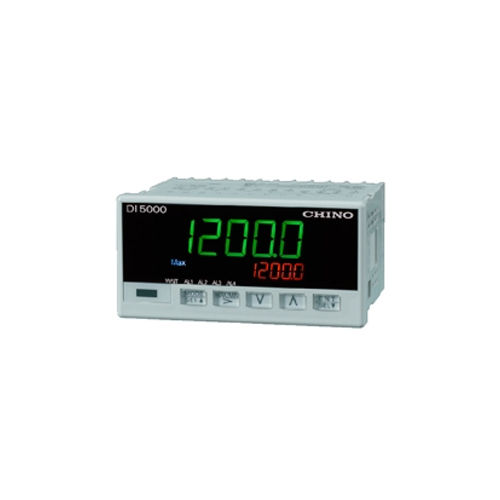
Di5000 Series Digital Indicator With Alarm Application: Commercial
MOQ10 Unit/Units
DisplayAnalog / Digital
Sensor TypeNormal
Product TypeDI5000 Series Digital Indicator With Alarm
Pressure TypeHigh / Medium
ApplicationCommercial
WarrantyYes
Chino Corporation India Private Limited
Navi Mumbai
Latest From Process Control Equipment & Instruments
CG Drive SK
By:
Onosef Controls Pvt. Ltd.
Beko Compressed Air Processing
By:
Super Tech Pumps And Equipments
Gas Cutter
By:
Excellent Enterprises
Digital Active Power Conditioner
By:
Syscon Enterprises
Flow Controllers
By:
Forbes Marshall Hyderabad Pvt Ltd.
Ready To Ship Process Control Equipment & Instruments
Most Popular Process Control Equipment & Instruments
Measurement and regulation of process variables in an industrial setting are the primary goals of the hardware and software that make up process control instruments. Mathematical models of manufacturing processes and systems are the basis for the development of control systems.
Common Process Control Equipment & Instruments
1. Level Control & Monitoring
Instrumentation for measuring and regulating flow tanks, vessels, and compartments can have their contents monitored, detected, and controlled via a control panel or monitor handled by a control engineer. If the current flow rate is too high or too low, the engineer can remotely control an electrical or mechanical actuator to make the necessary changes.
Orifice flow meters, turbine flow meters and Coriolis flow meters are all examples of devices used to regulate pressure in industrial settings.
2. Pressure Control & Monitoring
Using data from pressure sensors, pressure control systems monitor the pressure of a process and provide readings in Bar, KPa, or other applicable units. Mechanical or electrical pressure monitoring and control devices are available. In industries that work with pressured liquids, gases, or solids, they are indispensable equipment for preventing harm to workers and property.
3. Automated control Instrument
In order to better handle hazardous or precise industrial processes, automated control systems are increasingly being implemented. As long as the system is programmed to automatically adjust itself under different settings, a control engineer only has to examine automated control processes on a periodic basis to ensure that they are operating as intended. Because they remove the potential for human error, automated controls improve the consistency of highly repetitive industrial processes.
A catastrophic collapse can be avoided, however, with the help of high-precision equipment. Those in the Oil & Gas, Power Generation, and Air Quality industries can benefit from Makers' top-tier automation and control solutions.
4. Temperature Control & Monitoring Equipment
Instruments for measuring and controlling temperature detect shifts in the temperature of their surrounding environment or of the contents of containers, tanks, pipes, and other apparatus.
Modern Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) and P&ID systems allow the control and measuring instruments engineer to view temperature readings on a center console or monitor and make changes to one or more processing parameters, or shuttered equipment or the entire plant, to protect critical electrical failure or fire hazards.
5. Supervisory Controls & Data Acquisition
SCADA systems are used in a broad variety of sectors, including but not limited to power production, air purification, wastewater treatment, and manufacturing plants, to coordinate the various tools and systems used to keep tabs on and record data about these activities.
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) are used by SCADA systems for human interfacing and control, and feedback from sensors and PLCs is relayed to the control engineer.
What Are Process Control Equipment & Instruments?
The purpose of Process Control Equipment & Instruments is to keep an eye on the status of a process parameter, identify when it deviates from the ideal, and then take corrective action.
The ambient temperature, the pressure generated by the cooling water pumping system, and the voltage from the backup generator are all examples of process variables in control systems.
The process variable can only be regulated if its value can be measured and then transformed into a signal that the controller can respond to.
The operator enters or derives from another control calculation the desired value of the process variable, known as the setpoint. The deviation of the process variable from the setpoint serves as the control action's error signal.
Process Control Instruments List
- 1. Water Level Controller
- 2. Temperature Transmitter
- 3. Temperature Scanner Channel USB
- 4. Temperature Scanner
- 5. Synchronizer Card
- 6. Signal Isolators
- 7. Process indicators
- 8. Process Controller
- 9. Load Cell Controller
- 10. Jumbo display Indicators
- 11. Isolator
- 12. Flow Indicator
- 13. Fault Annunciate
- 14. Dual Process Indicator
- 15. Process Controller
- 16. Transducers
- 17. Sensors
- 18. Set Point
- 19. Discrete Controller
- 20. Analog Controller
- 21. Proportional Plus Integral Plus Derivative PID
- 22. Plus Integral Controllers PI
- 23. Control Loops
Working Principle Of Process Control Equipment & Instruments
1. Robustness , preference, Inner Stability, process symbiotic Attitude
Control should make use of the system's inherent dynamics as much as feasible, rather than forcefully influencing process values that are dependent on other variables. Having two people in charge at once always leads to chaos and instability.
Before doing anything else, control engineers should learn as much as they can about the system they are trying to regulate. The constant challenge prevents me from feeling like I've finally mastered something.
When the laws of physics are allowed to interact in a restricted spatial-temporal environment, unexpected phenomena can emerge.
2. Least use of controllers
As the number of controllers in a system increases, so does the chance of instability.
3. Lease use of instrumentation
Control is most tenuous at its instruments. When there are fewer instruments in play, there is less chance of failure or error.
4. Override Control
Multiple controllers and process variables can share responsibility for regulating a single manipulated variable with the help of override control. The same effect can be achieved with only a single controller by exchanging the mistakes that occur in the process variables.
The nonlinearity introduced by the changeover makes it possible that override control will create instability.
Transitional hiccups could be difficult to avoid. It is recommended to utilize a dedicated controller for each process variable unless they all have the same dynamics in the process.
5. Multiple Input control
By adjusting a single process variable, many controlled variables can be kept within their allotted ranges, as is the case with multiple input control.
The boiler steam outlet valve can be calculated using a number of different tuning parameters and temperatures. These include those at the economizer outlet, near the dry-out point, in the first segment of the preheater, at the real and goal stream, at the compression setpoint value and way of measuring, and at other points. I have seen it, so please don't laugh.
If one treats each variable separately, this strategy appears to have merit, especially for mathematical control engineers. When these factors are coupled, as they often are in complex processes, the behavior of the process can become unstable and difficult to predict.
It's important to provide this attractiveness with due consideration and support.
6. Multiple Controlled Input
In contrast to the single-control method, the input from several sources requires more attention. Many feedback loops and manipulated variables are all driven by the same controlled variable.
Maintaining the intended superheat level in a once-through boiler could be accomplished by adjusting the inbound water flow for slow modification of the water stock and dry-out point as well as the generator's output for quick and easy way of the temperature within the expected range.
Make sure there is enough room between the two operational domains, and figure out the dynamics to avoid resonances.
7. Model-based or Feed forward Control
By its very nature, model-based/feedforward control is robust and quick to recover from shocks. It prevents a negative impact from a disturbance on the process variables by making adjustments in advance.
Obviously, this is effective only if the model is stable and reliable enough to have a net beneficial effect on the control performance in general. Negligible control is guaranteed if these prerequisites are not met.
8. Negentropic, Lean Development
The physical universe has a built-in propensity toward increasing entropy over time. The concept of entropy is associated with the future, rather than the past. Notwithstanding this fatal fate, the world continues to advance thanks to the negentropic, the reverse-entropy force of correctly handled knowledge, one of the fundamental features of life.
Even when following best practices, control development often devolves into chaos as fixes pile up without ever getting to the root of the problems and as unused code remains in place.
The growth in code size over time is a quantifiable indicator of control's improving status. After all functionality has been delivered and commissioning and optimization have begun, the code volume should decline or at worst remain stable.
After an upgrade, either a current feature will be simplified, or a new feature of equal or greater complexity will replace an existing one.
Conclusion
Producing a high-quality product over and over requires stringent process control. Multiple materials, ranging from chemicals to physical objects, are used in any procedure. Automatic pipeline and product throughput adjustments made possible by process controls help maintain pipeline dependability, safety, and consistent oil or gas flow. Refineries utilize process controls to guarantee the security of workers, the quality of output, and the continuity of operations.
FAQs: Process Control Equipment & Instruments
Q. What are process control instruments?
Ans. Instrumentation for process control focuses on the monitoring and regulation of processes in an industrial setting. Scientific models of industrial systems and processes form the basis for control system design.
Q. What are the common instruments needed in the process control industry?
Ans. Here are some common instruments:
- Supervisory Control & Data Acquisition
- Pressure Control & Monitoring
- Temperature Control & Monitoring
- Level Control & Monitoring
Q. What are examples of process control instruments?
Ans. Some examples of process Control instruments are:
- Cooling Element with a Room
- Nuclear Power Plant Control Rod
- Desalination
- Cooking of Meat Products
Q. What is the cost of process control equipment & instruments?
Ans. The cost of process Control Equipment & instrument is between Rs 5,000- RS 5 lakhs.
Manufacturers & Suppliers of Process Control Equipment & Instruments
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Mifa Systems Pvt. Ltd. Ahmedabad, India | 18 Years |
Micon Automation Systems Pvt. Ltd. Ahmedabad, India | 18 Years |
Hindmedico Product Private Limited Howrah, India | 18 Years |
Silverline Metal Engineering Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai, India | 18 Years |
Ambetronics Engineers Pvt. Ltd. Mumbai, India | 16 Years |
Modern Traders Mumbai, India | 16 Years |
Procon Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Ahmedabad, India | 15 Years |
R. B Electronic & Engineering Pvt. Ltd. Chanod, India | 15 Years |
Nuclus Control Pune, India | 15 Years |
Nord Drivesystems Pvt. Ltd. Pune, India | 15 Years |
Popular Products