Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines
(4293 products)Product Showcase
Jardiance Tablet 25 Mg - Drug Type: General Medicines
522 INR (Approx.)/Box
MOQ10 Box/Boxes
Drug TypeGeneral Medicines
Physical FormTablets
DosageAs Per Suggestion
Dosage GuidelinesAs Per Suggestion
Suitable ForSuitable For All
Storage InstructionsDark & Dry Place
Darunavir tablets 600mg
Price: 8998.69 INR/Pack
MOQ10 Pack/Packs
Drug TypeOther Types
Physical FormTablets
FunctionAnti-Viral
Amphotericin B Injection I.P.
Price Trend: 250.00 - 270.00 INR/Piece
MOQ50 Piece/Pieces
Storage2 to 8 Degree Celcius
Expiration Date2 Years
Noxafil Schering Plough - Cas No: 171228-49-2
Price: 16810 INR/Piece
MOQ5000-10000 Piece/Pieces
Molecular FormulaC37H42F2N8O4
CAS No171228-49-2
DosageAs recommended by Physician
Medicine TypeAnti Fungal
StorageStore below 30AdegC
Drug TypeSpecific Drug
Vea Impex (i) Private Limited
Mumbai
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller10 Years
Axentri Maraviroc 150Mg Tablets - Grade: Medicine Grade
Price: 9900 INR/Bottle
MOQ1 Bottle/Bottles
StorageKeep in a Cool & Dry Place
GradeMedicine Grade
Dosage150 mg
Silde Nafil And D Apoxetine Tablets - Grade: Medicine Grade
Price: 1070 INR/Pack
MOQ100 Pack/Packs
UsageFor the treatment of both premature ejaculation and erectile dysfunction
GradeMedicine grade
StorageCool & Dry place
Dosage100 mg
Origin of MedicineIndia
Dosage FormTablet
Careclub Pharmaceuticals Llp
Mumbai
Revofer (Ferric Carboxymaltose) Injection Expiration Date: Oct 2022 Years
Price: 3000 INR/Bottle
MOQ50 Bottle/Bottles
Dosage500mg
Expiration Dateoct 2022 Years
Medicine Typeferric carboxymaltose
Biogen India
Delhi
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller9 Years
Azithromycin Tablets Ip `
MOQ1 Unit/Units
StorageDry Place
Medicine TypeTablet
DosageAs per doctor
Molecular Formula`
Centurion Remedies Private Limited.
Vadodara
25 Mg Tenofovir Alafenamide Tablets Expiration Date: 15-45 Months
MOQ10 Pack/Packs
DosageAs per doctor perception
StorageCool And Dry Place
AppearanceTablets
Usagepharmaceutical
Expiration Date15-45 Months
Quinine Hydrochloride API - 25 kg Pharma Grade, 99% Purity White Powder Antimalarial Medicine, IP/BP/USP Standards
Price: 7200 INR/Kilograms
MOQ25 Kilograms/Kilograms
Assay99
AppearanceWHITE POWDER
Medicine Typeantimalarial
CAS No130-89-2
Origin of MedicineINDIA
GradeIP/BP/USP
Liquid M-Proud-125 Injection
Price Trend: 125.00 - 155.00 INR/Box
MOQ10 Box/Boxes
Drug TypeInjection
Physical FormLiquid
Dosage125mg
Suitable ForTeenagers, Women, Adults, Aged Person, Suitable For All
Storage InstructionsStorage In Cool Place
Doxysafe Doxycycline 100 Mg Injection
Price: 560 INR/Vial
MOQ200 Vial/Vials
DosageAs directed by doctor
Medicine TypeInjection
Usagebacterial infections
Appearanceinjection
StorageCool & Dry Place
Safecon Life Sciences
Rudrapur
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller17 Years
Anti Cancer Injections - Storage: Cool & Dry Place
Price: 22250 INR/Piece
MOQ5 Piece/Pieces
DosageAs Per Suggestion
StorageCool & Dry place
Medicine TypeAnti Cancer Injection
UsageIndustrial
Origin of MedicineIndia
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Tablets Expiration Date: 3 Years
Price: 3900.00 INR/Tablet
MOQ10000 Tablet
AppearanceTablet
Expiration Date3 Years
Medicine TypeHIV
StorageDry & Cool place
DosageAs per doctor
Furosemide 40 Mg Tablet - Storage: Keep Dry & Cool Place
Price: 20 INR/Box
MOQ100000 Box/Boxes
AppearanceTablet
StorageKeep dry & cool place
DosageAs per physician
Sofosbuvir 400 mg Tablets
Price: 8500 INR/Bottle
MOQAs per requirement Bottle/Bottles
Drug TypeGeneral Medicines
Physical FormTablets
Recommended ForHIV and Anti Viral
DosageAs per doctor advice
Storage InstructionsDry and cool place
Mehadia Tradelinks
Mumbai
 Trusted Seller
Trusted Seller7 Years
Chlorhexidine Gluconate - 97% Assay, Clear Appearance | Surgical Hand Scrub and Healthcare Handwash for Patient Preoperative Skin Preparation and Overall Skin Cleansing
Price: 200 INR/Kilograms
MOQ440 Kilograms/Kilograms
DosageNA
GradeIP
UsageSANITIZER, MOUTHWASH
Expiration Date3 Years
StorageCOOL AND DRY PLACE
AppearanceCLEAR
Instgra Dolutegravir 50mg
Price: 1.00 USD ($)/Bottle
MOQ100 Bottle/Bottles
AppearanceWhite to off-white film-coated tablet
Salt CompositionContains dolutegravir sodium
Expiration Date24 months from the date of manufacture
UsageUsed in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection
Molecular FormulaC20H19F2N3O5
Pacakaging (Quantity Per Box)30 tablets per box
Antibiotics Medicines - Tablets, Recommended For Bacterial Infections | Highly Effective, Longer Shelf Life, Safe to Consume
Price Trend: 5000.00 - 10000.00 INR/Box
MOQ10000 Box/Boxes
DosageAs Prescribed By The Physician
Medicine TypeAntibiotics
GradeMedicine Grade
Expiration Date24 Months
StorageStore In Cold/Dry Place
Product TypeGeneral Medicines
Minocycline Tablets External Use Drugs
Price Trend: 3700.00 - 4800.00 INR/Piece
MOQ250 Piece/Pieces
Molecular FormulaC_{2} H_{2} 3
Purity99%
Formulations TypeExternal Use Drugs
Formulations FormTablets
Storage InstructionsStore in Cool
Favipiravir 400 Mg Tablet - Grade: Medicine
Price: 450 INR/Pack
MOQ100 Pack/Packs
StorageCool and dry
DosageAs per physician advice
GradeMedicine
AppearanceWhite tablet
Dosage FormTablet
Nimotuzumab Injection Grade: Medical Grade
Price: 29000 INR/Pack
MOQ10 Pack/Packs
GradeMedical Grade
Medicine TypeNimotuzumab Injection
StorageKeep dry & cool place
Dheer Healthcare Private Limited
Mumbai
Ciprofloxacin - 500mg Film-Coated Tablets | Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic for Bacterial Infections, Effective Against Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria, Suitable for Various Infections
Price: 80 INR/Strip
Medicine TypeCiprofloxacin 500 mg film-coated tablets
GradeBP
CAS No85721-33-1
Dosage250mg, 500mg
Molecular FormulaC17H18FN3O3
AppearanceTablets
Vitasv Pharma And Chemical Private Limited
Surat
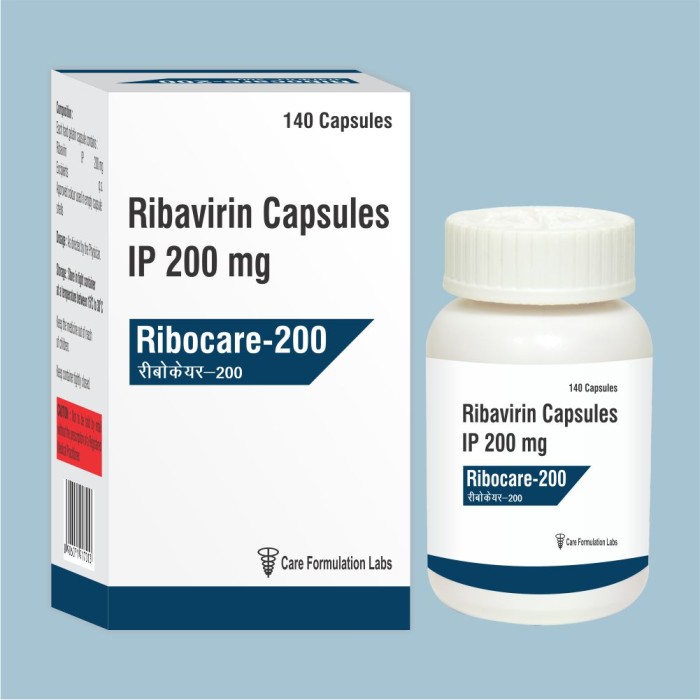
Ribavirin Ip 200Mg Cap - Dosage Form: Capsule
Price: 3800.0 INR/Pack
MOQ100 Pack/Packs
IndicationRiboflavin plays an important role in helping the body to break down the nutrients in food
Dosage FormCapsule
Pacakaging (Quantity Per Box)30 Capsule
Dosage30
Salt CompositionRibavirin
GradeMedicine Grade
Care Formulation Labs Private Limited
Delhi
HEALTHYLINEZO-600 Linezolide Tablets - 600 mg Antibiotic, 10x10 Oral Prescription Pack for Bacterial Infection Treatment, Safe & Effective
Price: 3600 INR/Box
MOQ10 Box/Boxes,
Molecular FormulaC16H20FN3O4
AppearanceTablet
UsageBacterial infection treatment
StorageCool & dry place
Dosage600 mg
Medicine TypeAntibiotic
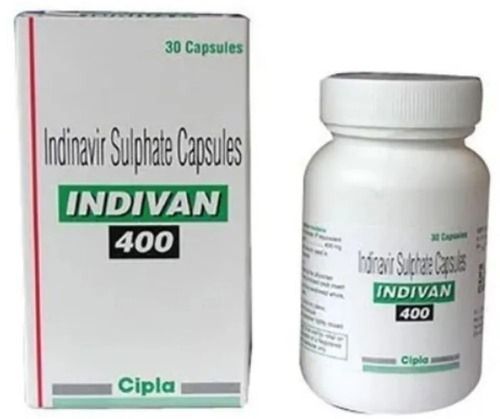
Indinavir Sulphate Capsules Cold & Dry Place
Price: 13 USD ($)/Pack
MOQ100 Pack/Packs
UsageTreatment of HIV infection
DosageAs Suggested by Doctor
StorageStore below 30AdegC
Drug TypeOther Types
Physical FormCapsules
Dosage GuidelinesAs Suggested
Cytonova Labs International Private Limited
Delhi
Viraday Tablets - Allopathic Medicine, 30 Tablets Box Packaging | Dosage: As Directed by Physician, Storage: Below 30°C, Protected from Light
Price: 3900 INR/Bottle
MOQ100 Bottle/Bottles
Medicine TypeAllopathic
StorageBelow Room Temperature 30AdegC, Protected From Light.
DosageDirected By The Physician.
3Mg Ivermectin Tablets - Storage: Cool & Dry Place
MOQ100 Bottle/Bottles
UsageIndustrial
Origin of MedicineIndia
AppearanceTablet
DosageAs Per Suggestion
StorageCool & Dry place
Drugs And Devices Pharma Private Limited
Valsad
Latest From Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines
Antibiotic Medicines
By:
Rajnikant & Bros.
99.9% Pure Medicine Grade Charak Cytozen Antibiotic Capsules
145 INR
By:
Ashlar Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.
Ready To Ship Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines
Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines: Classification
Anti-infective are pharmaceuticals used to treat or prevent infections; they can be categories into four types
a. Bacteria anti infective Drugs
b. Viruses anti infective drugs
c. Fungi anti infective Drugs
d. Parasites anti infective Drugs
Since their discovery, anti-infective have changed the medical field. They are now essential for treating and even preventing many different types of infection.
a. Aside from treating common colds and flu, antibiotics can also be used to treat and frequently completely eradicate more dangerous infections like pneumonia and tuberculosis.
b. Carry out both simple and sophisticated surgical procedures, including those with a high potential for infection such cesarean sections and joint replacements.
c. Chemotherapy and other immunosuppressive treatments are essential for cancer patients.
Antimicrobial resistance is a serious problem, reducing the efficacy of several anti-infectives (AMR).
Types of Anti-Infective Drugs & Medicines
1. Amebicides
Agents that kill or destroy amoebae are called "amebicides." Different types of amecides work in various ways. Humans and animals alike can benefit from their use, as they kill off amebae that cause disease.
2. Penicillins
Antibiotics called penicillins are isolated from the Penicillium fungus. When taken orally, antibiotics reduce or eliminate bacterial growth.
3. Oxazolidinon Antibiotics
The ribosomal 50S subunit of bacteria is targeted by oxazolidinone antibiotics, a type of synthetic antibacterial medicines. That's bad news because reproducing bacteria needs the 70S initiation complex to develop.
4. Miscellaneous Antibiotics
The term "miscellaneous antibiotics" refers to antibiotics that are the sole treatment option for their respective infections. Antibiotics from a wide variety of classes are used to treat illnesses brought on by bacteria and other organisms that are vulnerable to the drugs they are designed to combat.
5. Macrolide derivatives
Antibiotics belonging to the macrolide class are produced by streptomycetes. They are large-ring lactones found in nature, containing anywhere from 14 to 20 atoms in the ring. Macrolides prevent protein synthesis in bacteria by binding to the 50S component of the ribosome and blocking ribosomal translocation.
6. Lincomycin Derivatives
Protein synthesis is crucial to bacterial survival, and lincomycin derivatives are one of the few classes of antibiotics that work against this process. When dealing with infections caused by sensitive strains of pneumococci, staphylococci, or streptococcus, only lincomycin derivatives should be used.
7. Leprostatics
The expansion of Mycobacterium leprae, the bacterium responsible for leprosy, is slowed by leprostatic agents. Leprostatic agents can either actively kill the growing mycobacteria or they can inhibit bacterial growth, each with their own unique mechanism of action.
8. Glycylcyclines
Antibiotics in the glycocycline family prevent bacterial growth by interfering with the process of protein synthesis. They are effective against tetracycline-resistant bacteria as well as sensitive gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Antibiotics in the glycylcycline family are effective against bacteria that have developed resistance to other drugs. This includes MRSA, VRE, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, to name a few.
9. Glycopeptide antibiotics
Antibiotics belonging to the glycopeptide class prevent peptidoglycan production, hence preventing the development of bacterial cell walls. Infections caused by bacteria that are resistant to beta-lactams and other antibiotics, such as multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and enterococcal infections, can be treated with these drugs. As an added benefit, they can be utilized when a patient has an allergy to beta-lactams.
10. Cephalosporins
Antibiotics belonging to the cephalosporin class are generated from the fungus Acremonium, formerly known as Cephalosporium. Similar to penicillins, cephalosporins are bactericidal (kill bacteria).
11. Carbapenems
Beta-lactam antibiotics like carbapenems are effective against a wide variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, both aerobic and anaerobic. In 1976, the first carbapenem, thienamycin, was found. Antibiotics such as penicillin and cephalosporin are significantly weakened by the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes, often known as penicillinase. Carbapenems are famous for their ability to block these enzymes.
12. Antiviral Agents
Disease-causing viruses can be stopped in their tracks with the use of antiviral drugs. The window of time in which most antiviral drugs are effective is narrow, as viruses are often only active during replication. Since viruses share most of the metabolic processes of the host cell, finding treatments that are selective for the virus is challenging. Antiviral medications could be directed at viruses by targeting their unique enzymes.
13. Antituberculosis Agents
Chemotherapy for tuberculosis typically includes administering multiple medicines at once. Distinct drug classes inhibit the development of drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium because they target different aspects of the organism.
14. Linezolid
There is a new class of antibiotics called oxazolidinones, which includes linezolid. Indicated for the treatment of multidrug-resistant infections, it kills bacteria by blocking their ability to produce new proteins. Linezolid use during pregnancy has been reported in only one case study.
Anti Infective Drugs Uses & Side Effects
Anti Infective Drugs are normally administered orally. They can be injected or used topically by doctors to the infected area.
Anti Infective Drugs usually start acting within a few hours. For the best results, patients should take all of their prescribed medication as directed by their doctor.
It is more likely that the germs will develop resistance to future treatments if the drug is stopped before the whole course has been taken. The ones who make it through will have been exposed to the antibiotic and may develop resistance.
Even if your symptoms have subsided, it is still important to finish the full course of Anti Infective Drugs.
Instructions for proper dosing can be found in both the drug's accompanying booklet and your doctor's notes.
In order to make the most of Anti Infective Drugs, there are a few things people can do.
a. If you're taking metronidazole, don't drink alcohol.
b. If you're taking tetracyclines, it's best to avoid dairy items because they can interfere with the drug's absorption.
c. Consistent dosing occurs when medication is taken at the same time each day or at regular intervals throughout the day.
Side Effects:
1. Superinfections
Overuse of broad-spectrum antimicrobials can wipe out healthy bacteria. When normal flora bacteria are removed, opportunistic pathogens that were previously kept in check are free to penetrate tissues, causing an infection known as a superinfection.
2. Hypersensitivity Reactions
The vast majority of Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines are protein-bound, meaning they can be transported through the bloodstream and provoke antibody production in susceptible individuals.
3. Neurotoxicity
Certain antimicrobials, particularly those that tend to concentrate in certain organs or tissues, might cause damage to or interfere with the normal functioning of nerve tissue. Aminoglycoside antibiotics, for instance, have been linked to symptoms including wooziness, vertigo, and even hearing loss due to their tendency to accumulate in the eighth cranial nerve.
4. GI toxicity
A number of antimicrobials have toxic effects on the GIT lining, leading to gastrointestinal symptoms such nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis and liver failure can be caused by the harmful effects that some medicines have on the liver.
5. Kidney Damage
Aminoglycosides and other drugs have a direct toxic effect on the kidney's delicate cells, leading to renal impairment or even failure.
Anti Infective Vs Antibiotic
Anti Infective
Something with the ability to combat infections, either by slowing their progress or eliminating them entirely. The word "anti-infective" is broad enough to include drugs that kill not just bacteria and viruses but also fungi, protozoa, and worms. The term "anti-infective agent" refers to a class of medications used to combat infectious microorganisms that have invaded the human body.
Antibiotic
Antibiotics are prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with bacterial or fungal illnesses. When first discovered, antibiotics were substances made by one bacteria that selectively inhibited the growth of another.
Anti Infective Drugs Examples
a. Cephalosporins
b. Fidaxomicin
c. Nitrofurantoin
d. Carbapenems and monobactams
e. Clindamycin and lincomycin
f. Tetracyclines
g. Penicillins and β-lactamase inhibitors
h. Sulfonamides and trimethoprim
i. Quinolones
j. Pentamidine
k. Erythromycin and other macrolides
l. Aminoglycosides
m. Chloramphenicol
n. Glycopeptide antibiotics
FAQs: Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines
Q. Which antibiotic is good for all infections?
Ans: Antibiotics are not a panacea; they only treat certain infections. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial illnesses caused by pathogens like Strep., Staph.,or E. coli by directly killing the germs (bactericidal) or preventing further bacterial growth (bacteriostatic).
Q. What are the most common antibiotics?
Ans: Here are the most common antibiotics:
a. Penicillins
b. Cephalosporins
c. Tetracyclines
d. Fluoroquinolones
e. Macrolides
f. Glycopeptides
g. Sulfonamides
Q. What is Anti-Infective Drugs Market Size And Forecast?
Ans: Chemicals Used to Treat Infections At a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% between 2023 and 2030, the market is expected to increase from a 2022 valuation of USD 132.16 Billion to a 2030 total of USD 193.05 Billion.
Q. How can I become Anti-Infective Drugs suppliers in India?
Ans: Anti Infective Drugs production is a natural process that can now be mimicked and even improved upon in lab conditions, all thanks to scientific progress. Here are the steps to follows:
a. Must have a medical degree
b. Farm Registration
c. License
d. Hire an experienced business consultant
e. Choose the right equipment
f. Find a supplier
g. Make a website or brand
h. Jump on the B2b market place
Manufacturers & Suppliers of Anti Infective Drugs & Medicines
Company Name | Member Since |
|---|---|
Medico Remedies Ltd Mumbai, India | 19 Years |
Centurion Remedies Private Limited. Vadodara, India | 18 Years |
Schwitz Biotech Ahmedabad, India | 18 Years |
Safecon Life Sciences Rudrapur, India | 17 Years |
Lexicare Pharma Pvt. Ltd. Ankleshwar, India | 13 Years |
Dheer Healthcare Private Limited Mumbai, India | 13 Years |
P.B.P Enterprises Private Limited Mumbai, India | 13 Years |
Talent Health Care Ahmedabad, India | 11 Years |
Ambica Pharma Mumbai, India | 11 Years |
Healthy Inc. Mumbai, India | 11 Years |
Popular Products